Scaling AI: Managing Costs Effectively
Use FinOps, model tiering, Kubernetes, and governance to cut AI inference, storage, and GPU costs while maintaining performance and compliance.

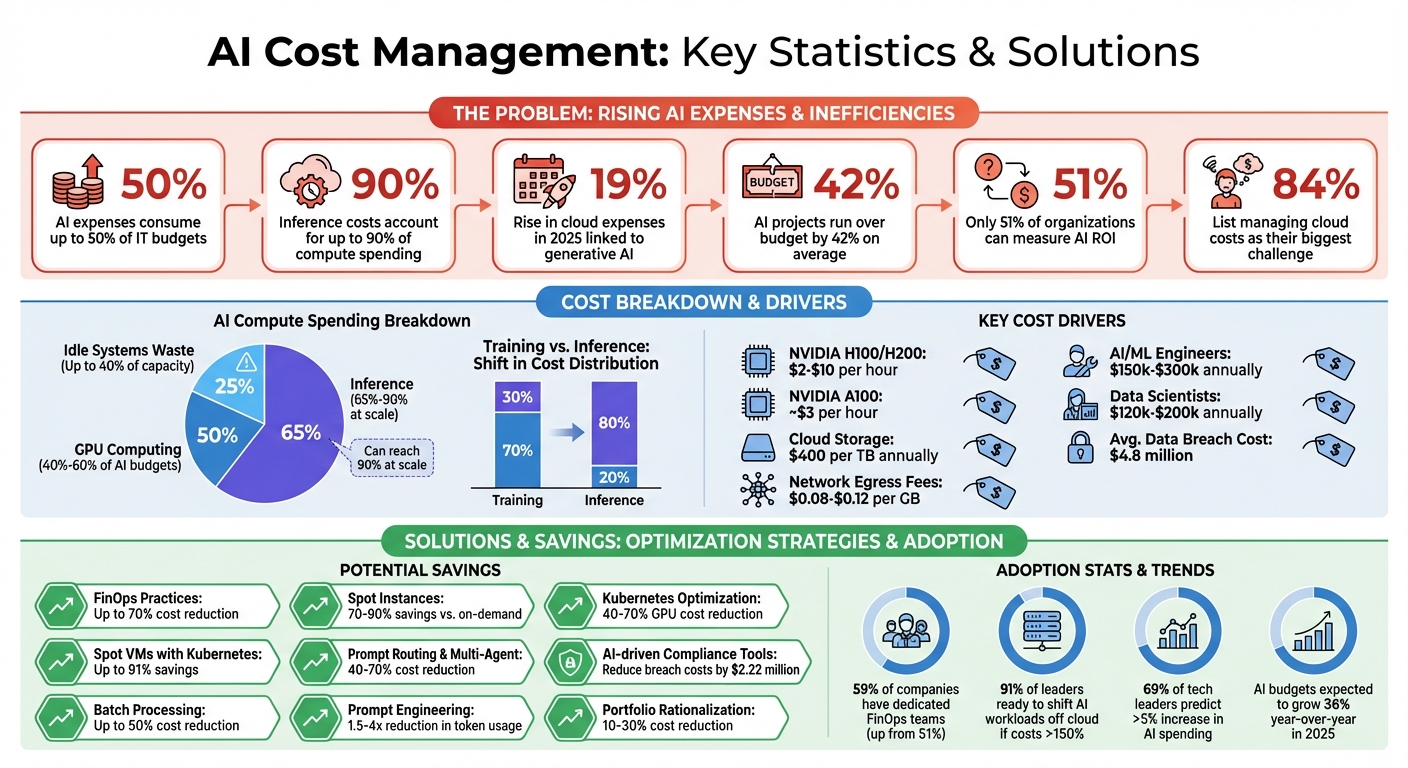
AI costs are rising fast, and managing them is now more critical than ever. Businesses report that AI expenses can consume up to 50% of IT budgets, with unpredictable spikes driven by cloud computing, model complexity, and infrastructure demands. For example, inference costs alone can account for up to 90% of compute spending. Without proper planning, these expenses can spiral out of control, eroding ROI and competitiveness.
Key Takeaways:
- Cloud costs are surging: A 19% rise in 2025 cloud expenses was linked to generative AI.
- Hidden costs add up: Data storage, compliance, and energy usage are often overlooked but significant.
- Solutions exist: Techniques like FinOps practices, Kubernetes optimization, and phased budgeting can cut costs by up to 70%.
To control AI costs:
- Track spending with tools like tagging and real-time dashboards.
- Use smaller, task-specific models for simple jobs and reserve larger models for complex tasks.
- Explore cost-saving infrastructure options like Spot instances and fractional GPU sharing.
- Invest in team training to reduce reliance on expensive new hires.
AI Cost Management Statistics and Savings Opportunities
Main Cost Drivers in AI Scaling
AI Infrastructure Costs
GPU computing eats up a hefty 40%–60% of AI budgets. What's interesting is how expenses shift as projects move from development to production. Training models, while costly, is often a one-time or periodic process. On the other hand, inference - using those trained models - now makes up about 65% of AI compute spending. For large-scale systems, this number can skyrocket to as much as 90%.
Hardware choices play a significant role in these costs. High-end GPUs like NVIDIA H100s or H200s can cost between $2 and $10 per hour on major cloud platforms. Mid-range options, such as the NVIDIA A100, are slightly easier on the wallet at around $3 per hour.
"Deploying a language model on an H100 when a T4 would suffice is like renting a stadium to host a poker night."
– Senior Machine Learning Engineer, Clarifai
Data storage costs are another financial hurdle. Cloud storage runs about $400 per terabyte annually, and as AI systems rely on ever-growing datasets, these costs can add up quickly. Then there are network egress fees - charges for moving data between regions or clouds - which range from $0.08 to $0.12 per GB. At scale, these fees can lead to some unpleasant surprises.
Operational and Maintenance Costs
Once the hardware is in place, the ongoing operation of AI systems becomes the next big expense. Scaling AI often demands frequent updates and architectural tweaks, sometimes within just a few months. Beyond infrastructure, keeping these systems running smoothly requires substantial engineering effort. Tasks like maintaining data pipelines, retraining models to ensure accuracy, and handling production issues all add to the cost.
Another challenge is resource efficiency. Idle systems can waste up to 40% of compute capacity. Mismanaged storage and "shadow IT" - spending on tech outside the control of IT leadership - worsen the problem. It's no wonder that 84% of organizations list managing cloud costs as their biggest challenge. Professional AI automation services can help mitigate these inefficiencies through optimized workflows. This has led 59% of companies to establish dedicated financial operations (FinOps) teams, a jump from 51% in 2024.
The rising costs are pushing companies to explore alternatives. For instance, 91% of data center leaders say they’re ready to shift AI workloads off the cloud if costs exceed 150% of what alternative hosting options offer. This is fueling a growing interest in hybrid and edge computing as ways to rein in operational expenses. as ways to rein in operational expenses.
Hidden Costs of Scaling AI
Scaling AI isn’t just about the obvious costs. Hidden expenses can sneak up and derail budgets. Take multi-agent systems, for example. These systems often face "coordination taxes", where repeated context sharing and redundant tool calls eat into efficiency gains.
Data-related costs are another area where budgets can spiral. Beyond storage, companies may face hefty bills for data licensing, legal reviews to ensure proper usage rights, and compliance with data retention laws. And then there’s the environmental toll: generative AI is projected to use 10 times more energy in 2026 than it did in 2023. Training a single ChatGPT model consumes as much electricity as 120 U.S. households use in a year. Cooling systems for AI infrastructure could require up to 1.7 trillion gallons of water annually by 2027.
Governance and security requirements add to the complexity. Companies need to implement systems to track autonomous decisions and meet regulatory standards, which means additional infrastructure and monitoring layers. Yet, only 51% of organizations can currently measure the ROI of their AI investments. This makes it tough to separate necessary compliance costs from unnecessary spending. With AI budgets expected to grow by 36% year-over-year in 2025, understanding these hidden costs is essential for keeping expenses under control.
Methods for Managing AI Costs
Using FinOps Practices for AI
With infrastructure and operational expenses climbing, FinOps practices provide a structured way to manage these costs effectively. FinOps, short for financial operations, equips AI teams with tools for real-time cost management through a three-step cycle: Inform (making expenses transparent with tagging), Optimize (adjusting resources for efficiency), and Operate (automating ongoing improvements). The FinOps Foundation explains:
"FinOps compliments DevOps by giving AI engineers, data scientists, and finance teams a common operating model for real-time cloud cost visibility, allocation, and optimization." – FinOps Foundation
One effective tactic is dual-signal autoscaling, which considers both performance metrics (like latency) and cost data. This prevents situations where achieving near-perfect model accuracy - such as 99% - leads to unreasonably high infrastructure costs. For example, StreamForge AI cut its AWS EKS bill in September 2025 by using Spot GPUs for non-critical tuning tasks and enforcing policy rules to reject pods without cost-center labels, boosting GPU utilization by 38%.
Granular tagging also plays a critical role. By adopting a consistent tagging system, every workload can be tied to a specific budget. Other practical methods include setting quorum thresholds to allocate GPUs only when predicted utilization exceeds 70%, switching from CSV to Parquet formats to reduce storage costs by 30%, and leveraging Spot instances for training tasks, which can save 70–90% compared to on-demand pricing.
These financial strategies pave the way for further cost-saving measures, such as the advantages Kubernetes offers over traditional cloud deployments.
Technology Optimization: Kubernetes vs. Traditional Cloud
Kubernetes provides a cost-efficient alternative to traditional VM-based setups by using containerization and precise resource sharing. Unlike VMs, which often allocate entire resources to single workloads, Kubernetes enables multiple workloads to share resources efficiently through bin packing. It also offers autoscaling tools like the Horizontal Pod Autoscaler, Vertical Pod Autoscaler, and Cluster Autoscaler to dynamically adjust resources based on demand, minimizing idle costs.
Using Spot VMs with Kubernetes can save up to 91% compared to standard compute VMs, while dynamic scaling can cut GPU costs by 40–70% compared to static provisioning. Tools such as Karpenter further enhance cost efficiency by selecting instances dynamically, while setting a Time-to-Live (TTL) of around 10 minutes for idle nodes helps avoid unnecessary charges. Additionally, workloads compatible with Graviton processors can benefit from savings of up to 20% and energy efficiency gains of 60% compared to x86 processors.
AI Agent Deployment for Cost Efficiency
Specialized AI agents offer another route to reducing operational expenses. By adopting multi-agent architectures - where agents are tailored to specific tasks like planning, retrieval, or analysis - you can avoid relying on a single, generalized model. When combined with prompt routing, which directs simpler queries to smaller models and reserves larger ones for complex tasks, this modular design can lower costs by 40–70%.
Finetuning vs. RAG comparisons show that Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) further enhances efficiency by grounding agents in external knowledge bases. This approach allows the use of models that are 5–10 times smaller without compromising performance. Since inference often accounts for 80–90% of total AI ownership costs, these optimizations can make a big difference.
NAITIVE AI Consulting Agency specializes in creating autonomous AI agents that incorporate cost-saving measures like fractional GPU sharing, prompt caching for frequently asked queries, and scale-to-zero architectures to handle fluctuating demand. They also use techniques like quantization (INT8 or FP16) and model distillation to develop leaner, faster models for production. For non-critical tasks, employing Spot instances can yield savings of 70–90%.
Maximizing Cost Efficiency of Generative AI Workloads
Managing Team and Skills Costs
Keeping team costs in check is just as important as managing infrastructure and operational expenses when building a scalable AI strategy.
Personnel costs often dominate AI budgets. For example, AI/ML engineers typically earn between $150,000 and $300,000 or more annually, while data scientists bring in salaries ranging from $120,000 to $200,000. Instead of hiring new talent, upskilling existing employees can be a smarter and more cost-effective option. Training programs for AI skills usually cost around $2,000 to $5,000 per employee - a fraction of the expense of onboarding new hires. Companies that dedicate 15–20% of their AI budgets to training and change management frequently report better returns on investment. However, it’s worth noting that 70–85% of generative AI projects fail, often due to human factors like lack of trust or insufficient preparation.
A hybrid staffing strategy can also work well. For instance, some companies bring in AI leaders on a consulting basis, paying $10,000–$30,000 per month for strategic guidance while relying on internal teams for execution. This approach allows organizations to move forward without committing to full-time hires. In production, staffing needs can be calculated based on infrastructure, such as one mid-level MLOps engineer for every 4–6 GPUs.
Phased Budgeting for AI Projects
Phased budgeting is a smart way to manage costs while proving the value of AI initiatives. In 2023, about 60% of AI budgets were focused on proof-of-concept projects. By 2026, this trend is expected to shift, with the majority of spending directed toward scaling and production. Breaking investments into phases - pilot, scale, and optimize - can lead to outcomes that are three to four times better than diving in all at once.
- Pilot Phase (10–15% of budget, 3–4 months): Focuses on validating a single high-value use case and setting up key metrics.
- Scale Phase (40–50% of budget, 6–9 months): Involves productionizing systems and building a fully capable team.
- Optimize Phase (35–50% of budget, ongoing): Prioritizes continuous improvement and maximizing returns.
| Phase | Budget Allocation | Duration | Primary Objective |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pilot | 10–15% | 3–4 months | Validate one high-value use case and establish metrics |
| Scale | 40–50% | 6–9 months | Productionize systems and build team capabilities |
| Optimize | 35–50% | Ongoing | Focus on continuous improvement and maximizing ROI |
Early adopters often spend 40–50% of their budgets on talent and training during the pilot phase. As they mature, they shift more of their spending toward infrastructure and operations.
Investing in Training and Change Management
As AI projects move from pilot to scale, investing in team development becomes essential for maintaining performance and achieving returns.
Interestingly, 50–65% of the work involved in tech transformations is administrative rather than technical. This highlights why training budgets are just as important as infrastructure investments. Companies should implement tiered training programs that include executive-level AI literacy, practitioner-level skills for teams like marketing and operations, and advanced technical training for specialists.
Managing change fatigue and easing concerns about job displacement are also key. Transparent communication about how AI will enhance, not replace, existing roles can help reduce resistance and encourage adoption. Some companies take a "use AI to fund AI" approach, redirecting savings - like cutting help desk costs by 30% with AI-driven tools - into further training and scaling efforts. Assigning cost ownership to specific teams, such as letting marketing manage its own AI pipeline expenses, can also drive accountability.
AI-related roles, like prompt engineers and AI product managers, often earn 20–40% more than their traditional counterparts. This makes internal upskilling not only cost-effective but also a way to retain talent. By aligning training investments with project phases, organizations can create a balanced, sustainable path for scaling AI.
Compliance and Reducing Hidden Costs
AI projects often run over budget - on average, by 42%. Add to that regulatory surprises, which can increase costs by 3–10%, and retrofitting compliance features, which can cost 3–5 times more than integrating them early on, and the financial risks become clear.
Meeting Security and Regulatory Standards
Starting with AI compliance in mind is critical for avoiding budget blowouts. For instance, one insurance company initially allocated $15,000 for compliance but ended up spending $240,000. The additional costs came from explainability requirements, bias audits, and data localization. Similarly, a healthcare AI project saw its change management costs balloon from $50,000 to $215,000 due to $40,000 in legal reviews and $35,000 for on-premise deployment to meet security standards.
For industries under strict regulations, compliance can take up to 8–12% of the total project budget, compared to the usual 3–5%. Designing models with interpretability features from the start avoids the steep costs of retrofitting later. Practices like data minimization - only collecting what’s absolutely necessary - reduce both regulatory risks and storage expenses. By embedding compliance into the project design, teams can create scalable AI systems without fear of unexpected costs. Additionally, tracking data origins (lineage) is essential to prevent costly retraining if data is later deemed unauthorized.
"Using unauthorized training data can cause long-lasting risks... potentially causing severe reputational or financial damage and requiring the model to be retrained or even retired from use."
– Google Secure AI Framework (SAIF)
Automating governance workflows can slash manual evidence collection time by 70–80%. Proactively addressing compliance also reduces the financial impact of data breaches. While the average cost of a breach in 2025 reached $4.8 million, AI-driven compliance tools can lower these costs by up to $2.22 million through early remediation measures.
Planning ahead for both regulatory requirements and unexpected expenses is vital to maintaining control over project costs.
Contingency Planning for Cost Volatility
Setting aside funds for unforeseen expenses is a smart move. For example, the scarcity of GPU-based hardware has made infrastructure costs unpredictable. Additionally, unauthorized AI usage, often referred to as "Shadow AI", can disrupt security policies and lead to expensive remediation efforts. Using Infrastructure as Code with multi-tiered alerts can help identify and address cost anomalies before they escalate.
To avoid being locked into high pricing, decouple agent logic from specific model providers. This flexibility protects against price hikes and ensures teams can switch providers if needed. Similarly, using smaller, task-specific models - like lightweight models for classification and larger ones for complex reasoning - can significantly reduce costs compared to defaulting to the most expensive options. For testing and development, temporary environments that automatically shut down after use can prevent unnecessary ongoing expenses.
"If cost control is not designed in from the beginning, teams typically end up retrofitting guardrails while the business is already depending on the system."
– Maisa AI
Assigning a "Directly Responsible Individual" (DRI) to oversee costs ensures someone is actively monitoring spending, identifying inefficiencies, and keeping budgets aligned with business goals.
Working with NAITIVE AI Consulting for Scalable AI Cost Management
NAITIVE AI Consulting Agency takes AI cost management to the next level with strategies tailored for scalable deployment. Managing AI costs effectively requires a mix of expertise and smart planning, and NAITIVE delivers with a focus on measurable results. Their approach, rooted in agentic AI principles, combines technical precision with a commitment to achieving clear business outcomes. Below, you'll find details on NAITIVE's customized strategies and the metrics that showcase their success in cost-efficient AI implementation.
Custom Strategies for Cost-Effective AI Implementation
NAITIVE uses a tiered model to customize AI solutions for different tasks. Instead of relying on large-scale models for everything, they deploy smaller, fine-tuned models for routine, high-volume tasks. Meanwhile, the more resource-intensive, large-scale models are reserved for complex, high-stakes operations. This targeted use of resources helps cut unnecessary computational costs.
Their approach to cost management spans several areas. For instance, NAITIVE's autonomous agent systems operate around the clock, reducing reliance on human oversight and lowering hiring expenses. Their AI voice agents are another standout example, with each call costing just $0.30 to $0.50 - significantly less than the $6.00 to $12.00 per interaction typical of traditional call centers. These AI agents also ensure 100% script adherence, compared to the 70–85% achieved by human agents, while eliminating turnover costs that can range from $10,000 to $20,000.
NAITIVE also provides managed services that continuously monitor and optimize AI deployments. This ensures cost efficiency and a strong return on investment (ROI) over time. Their consulting process starts with readiness assessments and architecture planning, which helps businesses meet security and compliance standards from the outset - avoiding the expensive fixes that come with retrofitting.
Examples of Scalable AI Success
NAITIVE's strategies deliver real-world results, offering businesses both operational and financial advantages. For example, traditional call centers often require 30–60 days to train agents, and their operations are limited to scheduled shifts. In contrast, NAITIVE's AI voice agents can be set up instantly and scale on demand, providing true 24/7 service. This is especially beneficial for businesses dealing with seasonal fluctuations or rapid growth, as it eliminates the delays and costs tied to hiring and training human staff.
The outcomes speak for themselves. NAITIVE's voice AI solutions have resulted in a 41% increase in conversion rates and a 34% improvement in customer retention. Their multi-agent systems handle complex workflows autonomously, freeing up human teams to focus on strategic priorities. By combining technical expertise with a deep understanding of business needs, NAITIVE transforms AI from a cost burden into a powerful tool for competitive growth.
Conclusion
Key Takeaways
Ignoring the costs of AI operations is a sure path to failure. The shift from traditional software economics to AI's operational model has made running costs the dominant factor in budgets. With inference driving most of the compute expenses, the days of "set it and forget it" infrastructure are long gone.
To manage costs effectively, focus on a few core principles. Building on FinOps practices, use AI-specific metrics like cost-per-token and GPU utilization instead of relying on outdated cloud KPIs. Implement model tiering to save money by assigning smaller models to simple tasks and reserving advanced models for more complex reasoning. Start with phased budgeting to demonstrate value before diving into aggressive cost optimization. Also, make cost management a priority by assigning clear ownership within teams.
"If cost is invisible, it's no one's problem. When it's visible, it becomes everyone's problem." - Nick Chase, Chief AI Officer, CloudGeometry
Technical strategies are equally important. For example, prompt engineering can reduce token usage by 1.5–4x, while batch processing through discounted asynchronous API calls can lower costs by up to 50%. Infrastructure tweaks like fractional GPU sharing and using spot instances - offering discounts of up to 90% - can turn unpredictable hardware expenses into manageable ones. These approaches set the stage for expert-led implementations. NAITIVE AI Consulting Agency specializes in designing scalable, cost-aware AI strategies, showing how smart cost management can be a competitive edge. Don’t overlook team and compliance strategies, which are just as crucial for sustainable AI scaling.
Next Steps for Businesses
To cut AI costs right away, start by logging key metrics to identify where your money is going. This visibility helps pinpoint high-cost areas and reveals which optimizations will have the most impact.
Next, audit your AI architecture with cost-saving levers in mind. Are you using expensive frontier models for tasks that simpler models could handle? Could you batch non-urgent requests through discounted APIs? Is your team tracking costs alongside performance metrics? These questions can uncover immediate savings opportunities. Companies that rationalize their AI portfolios using these principles often reduce costs by 10% to 30%.
For tailored strategies, consider partnering with NAITIVE AI Consulting Agency (https://naitive.cloud). With 69% of tech leaders predicting a more than 5% increase in AI spending this year, disciplined cost management could make all the difference. The time to act is now - before your next invoice arrives.
FAQs
Which AI cost metric should we track first?
To get a handle on your AI model expenses, start by tracking the total cost of ownership (TCO). This means accounting for everything - infrastructure, training, and inference costs. By doing this, you'll have a clear view of your overall spending. Knowing your TCO also helps pinpoint the areas driving up costs, making it easier to adjust and manage your budget efficiently.
When should we use a smaller model vs. a larger one?
Choosing the right AI model comes down to balancing cost, performance, and task requirements.
If you're looking for cost-efficiency and low latency, smaller models are a solid choice. They work well for tasks that don’t require extreme precision and can deliver results without consuming too many resources. On the other hand, larger models shine when handling complex tasks that demand higher accuracy, but they come with a trade-off: they require more resources and come with higher costs.
To make the best decision, consider these factors: How much accuracy do you need? What’s your budget? And how much latency can your use case tolerate? Matching your priorities to these considerations will help you find the right fit.
How do we reduce inference costs in production?
To reduce inference costs in production, there are several strategies you can implement:
- Right-size your GPUs: Match GPU resources to your specific workload requirements to avoid overspending on unnecessary capacity.
- Quantize models to INT4/INT8: Lower precision formats can significantly cut costs while maintaining acceptable performance for many applications.
- Batch requests: Process multiple requests together to make better use of computational resources.
- Switch to cost-efficient hardware: Consider using consumer GPUs or other affordable alternatives that meet your needs.
- Leverage distributed inference: Spread tasks across multiple devices to optimize resource utilization.
- Optimize API usage: Techniques like prompt engineering, caching, and routing can help minimize redundant processing and reduce overhead.
These methods allow you to strike a balance between performance and cost, keeping your operations efficient without compromising quality.




