How to Customize AI SLAs for Enterprises
How enterprises can design AI SLAs that measure accuracy, hallucination rates, compliance, tiered SLOs, and real-time monitoring to align AI with business goals.

AI SLAs (Service Level Agreements) are no longer just about uptime - they're about ensuring AI systems deliver accurate, reliable, and business-aligned results. Enterprises need tailored SLAs because standard agreements fail to address unique AI challenges like output quality, hallucination rates, and compliance risks.
Key Takeaways:
- AI SLAs must go beyond uptime: Include metrics like accuracy, precision, and response times.
- Custom metrics matter: Define goals based on your AI use case (e.g., chatbots vs. data analysis tools).
- Compliance and security: Address data governance, liability, and vendor accountability.
- Tiered SLAs: Differentiate service levels (e.g., Basic, Premium, and Enterprise tiers) with clear performance expectations.
- Proactive monitoring: Use real-time tools to track SLA compliance and prevent violations.
Example Impact: A telecom company improved customer satisfaction by 25% and saved $2M annually by implementing custom AI SLAs.
Tailored SLAs ensure AI systems align with business goals, reduce risks, and improve outcomes. The right metrics, escalation paths, and monitoring tools are essential to make this work.
Identifying Enterprise AI SLA Requirements
To get started, tie your operational goals to specific performance standards. This means moving past generic targets like uptime percentages and focusing on what your AI applications truly need to deliver. Align these SLA requirements with the AI lifecycle - Discover, Pilot, Scale, Embed, Govern - to ensure they evolve alongside your business needs. By doing this, you create a framework to evaluate both business impact and compliance.
Analyzing Business-Critical Needs
The first step is understanding your baseline costs before implementing AI. This gives you realistic performance benchmarks and a clear picture of what success looks like. Your SLA should focus on the areas that matter most to your business, not just system availability.
While traditional metrics like uptime and response time are still important, AI systems demand additional measures like accuracy rates (how well outputs match human-verified data), precision scores (e.g., F1 scores), hallucination rates for generative content, and relevance to user queries.
For example, a global telecom company in 2025 set specific SLOs: resolving 80% of inquiries within 30 seconds while maintaining 95% resolution accuracy. These efforts led to a 25% boost in customer satisfaction and $2 million in annual cost savings.
Define performance benchmarks for every scenario. AI systems need clear standards for query response times, processing throughput, and latency under various conditions. Keep in mind that 53% of users will abandon a service if it takes longer than 3 seconds to respond. Different tasks demand different performance levels - a real-time voice assistant might require sub-second latency, while batch processing tools can handle longer delays.
Also, include provisions for continuous improvement. Your SLA should specify model refresh cycles, retraining schedules, and timelines for resolving systematic issues or performance dips. This helps guard against model drift and ensures your AI systems remain effective over time.
Once your performance metrics are in place, focus on compliance and security requirements critical to your deployment.
Addressing Compliance and Security Standards
Your SLA should detail AI data governance and privacy standards from the outset. Clearly define where data can be stored and processed to meet regional regulations, set boundaries for data ownership (both input and output), and clarify whether providers can use your data for model training. If they can, require anonymization and safeguards to prevent those improvements from benefiting competitors.
Make sure to include audit rights. Don’t just rely on vendor reports - your SLA should explicitly allow independent monitoring and auditing of performance and compliance.
As Tony DiPadova from Clarative points out, "The SLA is just the beginning. The real protection comes from having the visibility to know when vendors aren't meeting their commitments and the operational discipline to hold them accountable".
Finally, address liability for AI-specific risks. This includes issues like algorithmic bias, intellectual property concerns tied to training data, and regulatory penalties. Your SLA should feature tailored liability caps and indemnification clauses that go beyond standard software agreements. Don’t forget to account for fourth-party risks - if one of your vendor's sub-providers (like a cloud service) causes an outage, your SLA should clarify who’s responsible and how such failures will be addressed.
Customizing SLA Performance Metrics and Tiers
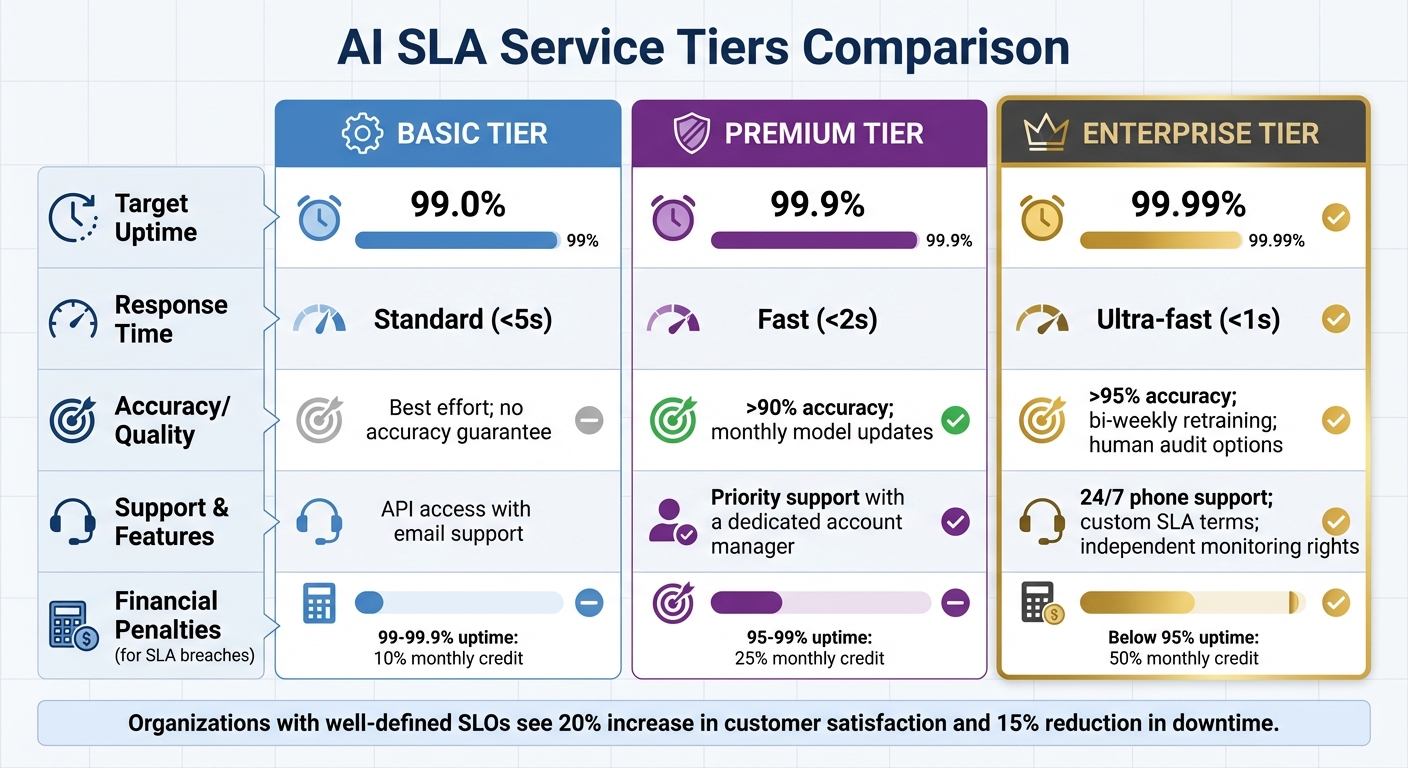
AI SLA Service Tiers: Basic vs Premium vs Enterprise Performance Standards
Once your AI system's compliance and security baselines are in place, the next step is to turn those requirements into measurable performance metrics. This ensures your AI systems deliver measurable results while allowing you to align service levels with your business priorities.
Defining Key Metrics for AI Systems
Start by identifying Service Level Indicators (SLIs) - the specific parameters you’ll monitor - before setting performance targets. While traditional metrics like uptime and response time remain essential, AI systems require additional measures to assess output quality and reliability.
Key metrics to include are:
- Availability: Monthly uptime percentage.
- Speed: Latency under three seconds.
- Reliability: Error rates for valid requests.
For AI-specific needs, add metrics like:
- Accuracy: Use F1 scores or precision measures.
- Hallucination Rates: Track the frequency of incorrect or fabricated outputs in generative models.
- Consistency: Measure output variance for identical inputs.
For instance, Google’s Document AI service defines downtime as any period where error rates exceed 10% over five minutes, highlighting that an AI system can technically be "up" but still fail to deliver meaningful results.
You should also include evolutionary metrics to account for ongoing improvements. Specify timelines for model refresh cycles, retraining schedules, and integrating user feedback into the system. To encourage innovation, consider implementing error budgets, which allow for a small margin of failure (e.g., 1% downtime) without penalizing development efforts.
Once these metrics are clearly defined, you can organize them into service tiers that reflect the importance of each AI application to your business.
Establishing SLA Tiers
Service tiers help prioritize metrics based on how critical each AI application is. For example, a customer-facing chatbot requires more stringent standards than an internal data analysis tool. These tiers should clearly differentiate the levels of service provided.
| Tier | Target Uptime | Response Time | Accuracy/Quality | Support & Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic | 99.0% | Standard (<5s) | Best effort; no accuracy guarantee | API access with email support |
| Premium | 99.9% | Fast (<2s) | >90% accuracy; monthly model updates | Priority support with a dedicated account manager |
| Enterprise | 99.99% | Ultra-fast (<1s) | >95% accuracy; bi-weekly retraining; human audit options | 24/7 phone support; custom SLA terms; independent monitoring rights |
To ensure accountability, attach financial remedies to these tiers. For example, you might offer credits of 10% of the monthly bill for uptime between 99% and 99.9%, 25% for uptime between 95% and 99%, and 50% for anything below 95%. For repeated violations or prolonged outages, consider escalating penalties rather than sticking to flat-rate credits.
Organizations that implement well-defined Service Level Objectives (SLOs) and tiered SLAs often see a 20% boost in customer satisfaction and a 15% drop in service downtimes. The key is to tie technical metrics to business outcomes - whether that’s boosting revenue per interaction, cutting costs per automated decision, or improving customer satisfaction. Aligning your SLA tiers with these goals ensures your performance metrics not only enhance operations but also deliver strategic value.
Configuring SLA Rules and Escalation Frameworks
Once you’ve established performance metrics and service tiers, the next step is setting up rules and escalation paths. These define how your organization reacts when AI systems fall short of targets, ensuring disruptions are handled swiftly and systematically to reduce their impact.
Defining Escalation Paths
Start by organizing incident response tiers based on severity, with clear timelines for acknowledgment, triage, and resolution. For instance:
- Critical issues: Acknowledge within 15 minutes, triage within 30 minutes, remediation plan within 2 hours, and mitigation within 4 hours.
- Major incidents: Acknowledge within 60 minutes and take initial action within 2 hours.
- Minor issues: Extend acknowledgment to 4 hours and triage to 8 business hours.
To ensure accountability, use a RACI matrix (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed). This assigns specific roles to every critical service. For example, the service owner may handle acknowledgment, the vendor’s contact might oversee triage, and executive sponsors stay informed during escalations.
AI-driven escalation frameworks can take this further by employing predictive analytics to identify potential breaches before they occur. These systems analyze ticket data, system logs, and user feedback to trigger proactive escalations. Companies using AI for SLA management have reported up to a 30% reduction in service costs while enhancing service quality. Automated escalation loops can also be set up, moving unresolved issues from on-call staff to backups, team leads, and eventually vendor executives.
To reinforce accountability, consider linking penalties to both availability and remediation speed. Vendors could face contractual consequences for delays in resolution or incomplete root-cause analyses, not just downtime. Testing escalation rules with historical ticket data can help confirm their effectiveness.
Combine these structured frameworks with automated, self-adjusting policies to address issues before they escalate.
Embedding AI Self-Adaptive Policies
AI systems can go beyond escalation by incorporating self-healing mechanisms that resolve performance issues without human input. For example, when SLA targets are at risk, AI can scale resources, restart services, or clear content delivery networks (CDNs) automatically. Organizations using solutions like MSARS (Meta-learning for Smarter Autoscaling) have seen 38% fewer service-level objective (SLO) violations compared to traditional methods.
Error budgets can also act as triggers for governance. If failures exceed predefined limits, development teams are prompted to address issues while still fostering innovation. By 2026, 63% of enterprises plan to integrate AI into contract compliance workflows, highlighting the shift toward autonomous SLA management.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) can further enhance this process by evaluating ticket urgency and complexity, ensuring high-risk issues get routed to senior experts immediately. In industries with strict regulations, AI systems should provide "reason codes" and timestamps for every automated action, maintaining transparency and auditability.
To make these policies dynamic, define them in machine-readable formats like YAML. For example, a breach condition such as forecasted availability dropping below 99.5% can trigger automated actions. These "living agreements" adapt in real time to operational demands, moving away from rigid contracts. Predictive analytics powered by AI can help prevent up to 70% of SLA violations, making these self-adaptive policies a critical part of maintaining service quality.
Monitoring, Adapting, and Governing AI SLAs
Finalizing an AI SLA framework isn’t just about setting it up - ongoing monitoring and governance are key to keeping performance on track. By combining defined metrics with escalation protocols, real-time monitoring ensures SLAs consistently deliver operational value.
Implementing Real-Time SLA Monitoring
To make SLA monitoring effective, start by converting SLA documents into machine-readable formats. With tools like NLP models, you can parse contracts in formats like PDF or DOCX and extract measurable obligations - such as "99.5% availability" - into structured schemas. These obligations can then be tied to real-time metrics like latency, CPU usage, or API throughput within your observability tools.
Proactive monitoring has proven benefits: it boosts uptime by 25%, reduces manual checks by 70%, and cuts SLA violations by 45%. Additionally, AI-driven monitoring can lower false alarms by 80%, significantly improving the accuracy of incident responses.
Beyond uptime, it’s important to track Behavioral SLAs. These focus on the quality of AI outputs, such as accuracy, tone, and ethical alignment. For systems with multiple AI agents, use Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) to map dependencies and understand how one agent’s failure might impact others downstream. To avoid excessive alerts, set anomaly detection thresholds at 95% confidence or higher, and implement circuit breakers to either fail fast or reroute to human operators when upstream AI services falter.
Once obligations are extracted and mapped to real-time metrics, integrate these with ITSM platforms like ServiceNow or Jira. This allows for automated ticket generation and compliance tracking. Additionally, you can automate monthly compliance reports that align with the terms in legal contracts, ensuring audit readiness.
"AI-driven predictive analytics allows SLA monitoring to move from reactive firefighting to proactive prevention, helping enterprises avoid up to 70% of potential SLA violations".
These advanced monitoring practices lay the groundwork for effective SLA governance and adaptable penalty frameworks.
Negotiating SLA Terms and Governance Policies
Governance starts with auditability and transparency. Ensure the right to independent measurement and third-party monitoring instead of relying solely on vendor dashboards. Use timestamped action logs for every AI decision and store prompt-response pairs to maintain a clear and accessible audit trail.
With transparent measurement in place, focus on negotiating detailed governance policies to enforce accountability. Introduce escalating penalties for recurring SLA breaches instead of relying on flat credits. Consider using error budgets, which allow for a predefined level of failure while balancing reliability with the flexibility needed for AI advancements. Companies that implement well-defined SLOs and SLAs often see a 20% increase in customer satisfaction and a 15% reduction in service downtime.
Set up a cross-functional governance board to oversee AI changes across environments. Use tools like feature flags and canary releases to manage updates safely. Require human oversight for high-stakes decisions - like financial transactions or disciplinary actions - and conduct audits after "near-miss" SLA events to identify improvement areas. Embed SLA monitoring into CI/CD pipelines to ensure model updates don’t disrupt existing service commitments. Treat every AI dependency as a versioned product with assigned owners, clear deprecation policies, and automated remediation playbooks stored in Git for rapid rollbacks.
Conclusion
Final Thoughts
Customizing AI SLAs goes beyond the basics of uptime metrics, focusing instead on critical factors like accuracy, precision, and hallucination rates. AI outputs, by their very nature, are probabilistic, making them inherently unpredictable.
Effective AI SLAs tackle challenges like model drift by incorporating regular retraining, continuous monitoring, and well-defined data governance practices that clarify input ownership and AI-generated insights. These strategies not only help maintain quality but also enhance efficiency and improve customer satisfaction. By introducing error budgets, organizations can strike a balance between innovation and reliability.
"Our AI chatbot was technically 'up' 100% of the time last quarter, but it was giving nonsensical answers to 35% of customer queries... the signed SLA considered such results a success, but our business users considered it a failure." - VP of Customer Success
When done right, the impact is clear: a 70% boost in efficiency and customer satisfaction when AI is used for service optimization. The key is to focus on meaningful outcomes and avoid misleading metrics - like the Watermelon Effect - where surface-level "green" metrics mask deeper performance issues. By leveraging the performance metrics, escalation protocols, and adaptive policies discussed earlier, enterprises can fundamentally reshape how they enforce and gain value from AI SLAs.
How NAITIVE AI Consulting Agency Can Help

NAITIVE AI Consulting Agency specializes in helping businesses build and manage AI SLAs that deliver real accountability and measurable success. With a blend of technical know-how and business acumen, we guide you through every step: assessment, design, integration, and optimization of your AI SLAs.
We assist in setting realistic performance baselines, creating tiered standards for various use cases, and embedding SLA monitoring directly into your CI/CD pipelines. Whether you're deploying autonomous AI agents, voice automation tools, or complex business workflows, we ensure your SLAs are aligned with actual business objectives - not just technical uptime. Our team is dedicated to crafting dynamic, adaptable agreements that evolve alongside your AI systems. Reach out to NAITIVE AI Consulting Agency to develop AI SLAs that deliver accountability and measurable results.
FAQs
Which AI quality metrics should our SLA include?
Key metrics to evaluate AI performance in your SLA include:
- AI decision accuracy: Measured through precision, recall, and F1 scores to gauge how well the AI makes decisions.
- User satisfaction scores: Metrics like CSAT (Customer Satisfaction Score) and NPS (Net Promoter Score) to assess user experience.
- System processing speed: Factors such as response time and latency to ensure quick and efficient performance.
- MTTR (Mean Time to Resolution): Tracks the average time it takes to resolve issues.
- One-contact resolution rate: Measures the percentage of issues resolved in a single interaction.
- Error reduction rate: Evaluates how effectively the AI minimizes errors over time.
- Cost per interaction: Helps monitor the financial efficiency of AI-driven processes.
These metrics collectively provide a comprehensive view of AI performance, reliability, and the overall user experience.
How do we measure hallucination rates in production?
To gauge how often hallucinations occur in production, calculate the percentage of AI responses that include made-up or incorrect information. Use specific metrics to spot inconsistencies by comparing AI outputs to reliable source data. A mix of automated scoring tools and human evaluation can help refine accuracy. Keeping an eye on these metrics and logging instances where responses stray from verified facts is key to maintaining AI dependability and lowering hallucination rates in enterprise use cases.
What audit rights should an enterprise AI SLA require?
An enterprise AI SLA should grant audit rights to monitor and verify the AI system's performance and adherence to contractual terms. These rights should cover areas like data processing, model updates, and the AI system's overall behavior. This ensures a level of transparency and accountability while confirming the system aligns with the agreed-upon metrics. Regular audits are especially important for tracking changes in model behavior and ensuring compliance throughout the AI system's lifecycle.




