5 Resource Allocation Models for Hybrid AI Systems
Five hybrid AI allocation models: RL, predictive analytics, autonomous routing, auto-scaling, self-healing. Reduce cloud costs and boost throughput.

Hybrid AI systems combine local Small Language Models (SLMs) with cloud-based Large Language Models (LLMs) to optimize costs, performance, and scalability. The right resource allocation strategy can reduce costs by up to 30%, improve task accuracy, and handle enterprise-scale demands efficiently. Here’s a quick breakdown of five key models:
- Reinforcement Learning-Based Allocation: Dynamically learns to split tasks between local and cloud resources, cutting costs by up to 30% and boosting performance.
- Predictive Analytics-Driven Allocation: Anticipates resource demands using historical data, reducing cloud expenses by 30–50% and ensuring smooth operations during traffic spikes.
- Autonomous Workload Distribution: Automatically routes tasks in real time, reducing costs and maintaining accuracy within 2–5%.
- AI-Powered Auto-Scaling: Proactively adjusts resources based on demand, lowering latency and improving resource utilization.
- Self-Healing Resource Optimization: Detects and fixes resource issues autonomously, ensuring uninterrupted service and reducing repair costs.
Each model addresses specific challenges in balancing cost, scalability, and performance, making hybrid AI systems more efficient and reliable for enterprises managing millions of AI requests monthly.
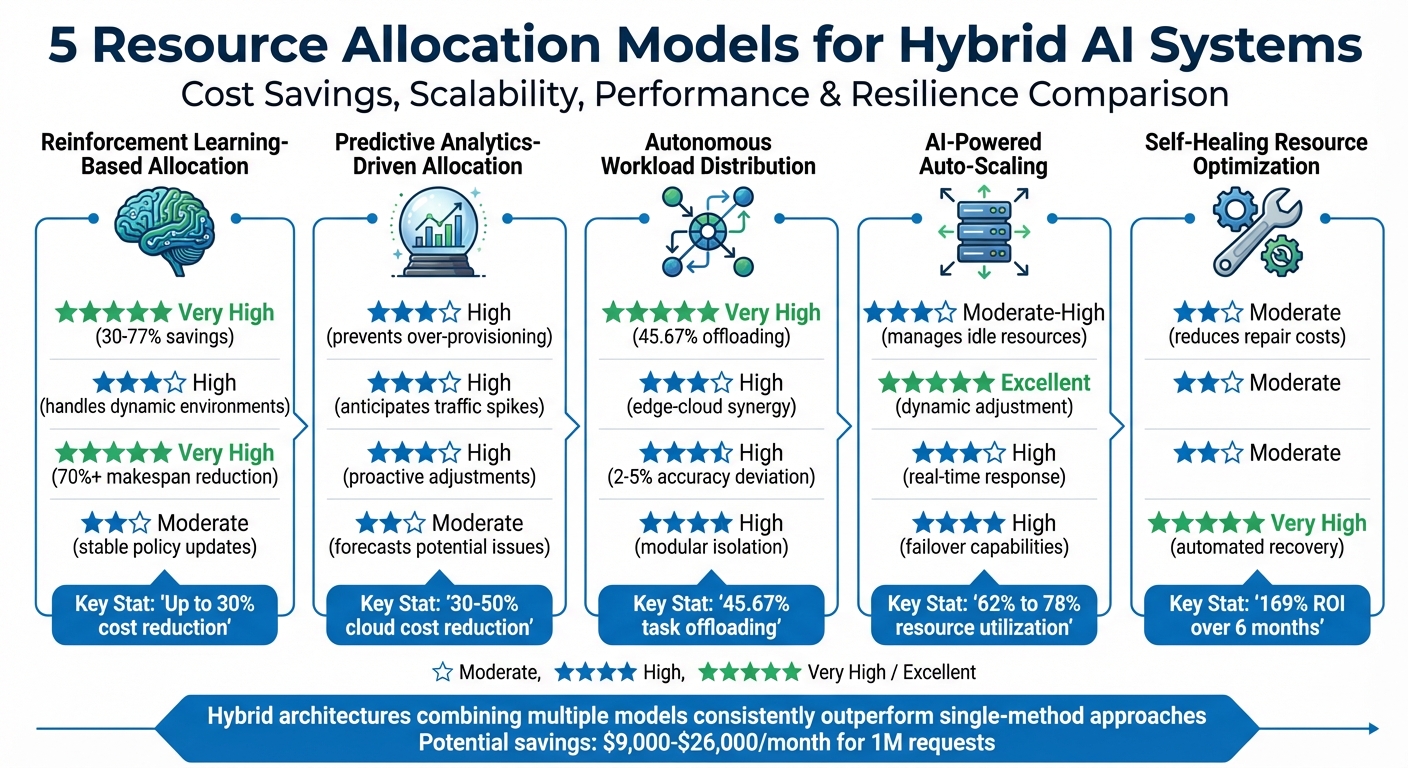
Comparison of 5 Resource Allocation Models for Hybrid AI Systems
How Flawless AI simplified operations with Amazon EKS Hybrid Nodes | Amazon Web Services
1. Reinforcement Learning-Based Allocation
Reinforcement Learning (RL) approaches resource allocation as a Markov Decision Process, where an AI agent learns to make strategic decisions over time rather than simply reacting to immediate demands. Think of it like a chess player carefully planning moves, considering not just the immediate benefit but the long-term impact. In hybrid AI systems, this translates to dynamically dividing tasks between local Small Language Models and cloud-based Large Language Models, continuously refining strategies based on real-world feedback.
The system uses a multi-objective reward structure to balance competing priorities: meeting Service Level Objectives (SLOs), minimizing cloud API costs, and reducing energy consumption. A key feature here is convergence detection, which identifies when a cheaper local model can deliver results comparable to a more expensive cloud model. This allows for intelligent offloading without compromising quality. The result? Substantial cost savings and smarter resource allocation.
Cost Efficiency
RL systems can deliver up to 30% savings in operational costs compared to cloud-only setups. For example, researchers Biman Barua and M. Shamim Kaiser demonstrated in December 2024 that an RL-based framework for microservices achieved 30-40% cost reductions compared to traditional threshold-based scaling. This could lower a $9,000 monthly bill to around $6,300.
"HERA achieves a crucial balance by decreasing operational costs by up to 30% through an allocation of 45.67% of subtasks to local hardware, all while preserving accuracy." – Shiyi Liu, University of Virginia
Advanced hierarchical RL systems take this even further. By splitting responsibilities between a high-level agent (managing service placement) and a detailed scheduler (handling CPU/GPU quotas), these systems can cut costs per 10,000 requests from $6.80 to $4.62, all while maintaining 98.6% compliance with SLOs. Beyond just saving money, RL systems also excel in handling scalability.
Scalability
RL is built to manage growth efficiently, using nonlinear models like multi-layer perceptrons to handle massive state spaces that traditional methods would struggle with. Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) takes things a step further by distributing the learning process across multiple agents, enabling decentralized decision-making that scales horizontally. This approach boosts resource utilization efficiency by 20-30%, allowing systems to adapt to growing workloads without requiring a complete overhaul. Such scalability is crucial for maintaining high performance in enterprise environments.
Performance Optimization
Unlike traditional methods that assume static conditions, RL adapts continuously to changing demand patterns - whether it’s handling a flash sale or an unexpected traffic surge. In the same December 2024 study, RL reduced latency by 15-20% during peak periods. It’s particularly effective at managing transient conditions and switching delays that classical queuing theory struggles to address.
"RL can automatically learn high-quality management policies without an explicit performance model or traffic model, and with little or no built-in system specific knowledge." – Gerald Tesauro, IBM Research
Resilience
For enterprise operations, resilience isn’t optional - it’s essential. RL ensures robustness with safe exploration techniques like constraint shielding, which prevent the AI from making decisions that would violate strict performance requirements. Modern frameworks also use offline warmstarts, training on historical data to avoid poor performance during the system’s early learning phase. In real-world tests, RL frameworks have shown a 31.2% increase in utilization and a 24.8% reduction in costs across industries like healthcare and finance.
The decentralized nature of Multi-Agent RL adds another layer of reliability. If one component fails, the system prevents cascading issues by redistributing tasks, ensuring stability even under challenging conditions.
2. Predictive Analytics-Driven Allocation
While reinforcement learning adapts to changes in real time, predictive analytics takes a forward-looking approach, anticipating future resource demands. By analyzing historical data and applying machine learning techniques, predictive analytics forecasts what resources will be needed and when. This allows systems to prepare for peak usage periods and potential resource shortages well in advance. Instead of scrambling to address a sudden spike in traffic, predictive models foresee the surge and adjust resources ahead of time.
In hybrid AI systems, this capability helps determine whether specific tasks should be executed on local Small Language Models (SLMs) or cloud-based Large Language Models (LLMs) before they are run. These models use feature-wise attention mechanisms to focus on critical resource metrics - such as network traffic or disk I/O - that act as early indicators of increased demand. Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (BiLSTM) models, for instance, can detect workload spikes 200ms faster than reactive methods, maintaining 94.6% SLA compliance even during high traffic periods. This proactive approach complements dynamic task allocation by ensuring resources are adjusted in advance.
Cost Efficiency
Predictive models not only ensure smooth operation but also help cut costs. By anticipating resource needs, these systems optimize spending before demand surges. For example, predictive allocation can reduce cloud expenses by 30–50%, translating to monthly savings of $9,000 to $26,000 for 1 million AI requests. They also identify and eliminate "zombie" resources - idle infrastructure that continues to incur costs - during low-demand periods. The financial benefits are quick to materialize; in a deployment of 10,000 virtual machines, predictive frameworks can achieve ROI in just 2.7 months.
Scalability
Predictive analytics supports seamless growth, even in massive infrastructures. With decentralized multi-agent architectures, these systems avoid the bottlenecks that plague centralized setups, enabling linear scalability across environments with 5,000+ nodes. Unlike reactive systems, which become less effective as infrastructure expands, predictive models maintain sub-100ms decision latency regardless of cluster size. This is achieved through distributed observers that monitor resource metrics across the system and provide forecasts to local decision-makers without overloading a central controller. The result? Over 90% resource efficiency through dynamic scaling, compared to the less-than-60% efficiency seen in traditional methods.
Performance Optimization
By predicting demand patterns, systems can significantly boost performance. Bidirectional forecasting models analyze historical trends to anticipate future needs, achieving 94.56% prediction accuracy with an inference time of just 2.7ms. This speed advantage translates into real-world benefits: predictive frameworks improve throughput by an average of 38.7% and reduce energy consumption by 42.3% compared to traditional scheduling methods. They also optimize task routing by assigning simpler tasks to rule-based logic or local SLMs, while reserving expensive cloud-based LLMs for more complex processes. This approach ensures high performance while keeping costs in check.
Resilience
Predictive analytics enhances resilience by preparing for a range of potential scenarios. Through scenario planning, it creates contingency models to ensure resources remain available, even when demand shifts unexpectedly. When resource shortages are anticipated, the system makes adjustments before problems arise. This "self-healing" capability can restart services or reallocate resources automatically, without requiring human intervention. Such proactive measures reduce SLA violations by up to 72% compared to reactive approaches. Combined with real-time monitoring, predictive analytics identifies and addresses bottlenecks as they develop, preventing disruptions before they occur. This strengthens the hybrid AI model and ensures reliable resource management.
3. Autonomous Workload Distribution
Autonomous workload distribution takes the guesswork out of deciding where AI tasks should run by making those decisions automatically - no human input required. Instead of relying on rigid rules or fixed thresholds, these systems use intelligent schedulers to split workloads between local Small Language Models (SLMs) and cloud-based Large Language Models (LLMs) in real time. The magic happens at the subtask level, where each step in a complex AI agent's reasoning process is analyzed to determine the most efficient execution environment. This approach works hand-in-hand with reinforcement learning and predictive analytics, enabling precise, on-the-fly task routing.
In April 2025, researchers showcased this concept with HERA, a system that paired a local Mistral-7B model with cloud-based GPT-4 running on Nvidia RTX 4090 GPUs. The results? HERA offloaded 45.67% of subtasks to the cloud, reduced operational costs by up to 30% for 1 million monthly requests, and kept accuracy deviations within a tight 2–5% range.
Cost Efficiency
By leveraging autonomous decision-making, these systems bring significant cost savings. They route straightforward tasks to local hardware, reserving cloud resources for more complex processes. For instance, GPT-4o costs $0.01 per 1,000 prompt tokens, and frequent cloud API usage can quickly rack up bills - small businesses often pay over $9,000 monthly for enterprise-level ChatGPT services. Autonomous systems track the "S-L distance" (the difference in output quality between SLMs and LLMs) to decide when local processing is sufficient. For example, when cosine similarity exceeds 0.7, the system sticks to the cheaper local model, avoiding unnecessary cloud expenses.
Scalability
These systems are built to grow with demand, thanks to their modular, multi-agent architectures. This design allows specialized agents to be added or updated without overhauling the entire system. Multi-cluster optimization further boosts resource efficiency, improving utilization rates from 62% to 78% - a 25% increase compared to traditional reactive methods. They also excel at load balancing, with scores improving from 0.71 to 0.88, ensuring tasks are evenly distributed across the infrastructure. By moving to unified control planes, they achieve global oversight and eliminate the resource fragmentation that often plagues siloed systems.
Performance Optimization
Intelligent task routing doesn’t just save money - it speeds things up too. Autonomous systems can cut average response times from 245ms to 185ms in multi-cluster setups. Early-stage subtasks are handled locally, while cloud resources are reserved for more demanding reasoning tasks. Hardware-level enhancements, like Intel DL Boost with VNNI, can further boost AI inference performance by 1.64X in hybrid environments. These systems also improve stability, reducing deployment disruptions from 6.4 to 3.1 events per hour, ensuring smoother operations.
Resilience
Beyond cost and performance benefits, autonomous workload distribution strengthens system resilience. Hierarchical classifiers and multi-cluster isolation ensure mission-critical tasks remain operational, even during failures. A two-step classification process first determines whether a task can be handled locally, then breaks down complex reasoning into subtasks for optimal distribution. Critical agents are equipped with high-availability setups and failover mechanisms, while less critical tools use standard configurations to keep costs manageable. If a cluster goes down, the system automatically shifts workloads to other geographically dispersed clusters, maintaining uptime without human intervention. Continuous feedback loops, powered by telemetry and predictive learning, help the system adapt quickly to workload changes, avoiding cascading errors that can arise when subtasks are treated in isolation.
4. AI-Powered Auto-Scaling
AI-powered auto-scaling takes resource management to the next level by predicting demand and allocating resources in advance. Instead of simply reacting when CPU usage crosses a certain threshold, these systems analyze historical data and real-time trends to anticipate traffic surges. This allows resources to be provisioned proactively, ensuring smooth operations during spikes in demand. In hybrid AI setups, this technology dynamically chooses between local Small Language Models (SLMs) and cloud-based Large Language Models (LLMs), depending on the complexity of the task at hand. By seamlessly integrating with earlier strategies, this approach boosts both cost efficiency and system responsiveness.
Cost Efficiency
One of the standout benefits of AI-powered auto-scaling is its ability to drive down costs. By intelligently routing tasks, these systems can slash operational expenses by as much as 30% for hybrid deployments. For example, handling 1 million monthly requests with this method could result in significant savings. AI gateways enforce global token caps, preventing excessive costs from runaway autonomous agents. Regular monthly reviews help identify areas of "cost creep", such as instances where premium models like GPT-4o (at $0.01 per 1,000 prompt tokens) are used for tasks that simpler, more affordable SLMs could handle. Specialized models like IBM Granite can deliver over 90% savings compared to general-purpose options when tasks are matched appropriately.
Scalability
AI-powered auto-scaling excels in managing scalability by ensuring resources are allocated in real time based on demand. This dynamic optimization improves resource utilization from 62% to 78%, representing a 25% gain over traditional reactive methods. It also enhances cross-cluster load balancing, with scores improving from 0.71 to 0.88, ensuring tasks are evenly distributed across global infrastructure. Tools like Karpenter fine-tune compute resource provisioning, eliminating waste. By combining horizontal scaling (adding more instances) with vertical scaling (adjusting instance size), these systems efficiently handle both traffic surges and complex workloads. The result? Lower latency and faster service delivery.
Performance Optimization
When it comes to performance, AI-powered auto-scaling delivers tangible improvements. In multi-cluster environments, average response latency drops from 245 ms to 185 ms. Advanced algorithms like ATSIA3C reduce task completion times (makespan) by an impressive 70.49% compared to traditional methods. Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) techniques improve execution time by 35–45% over random offloading strategies, while Rainbow Deep Q-Network models boost energy efficiency by 29.8% and cut latency by 27.5% in edge-cloud setups.
Resilience
Beyond efficiency and performance, auto-scaling enhances system resilience by maintaining stability during peak demand. Deployment instability events are reduced from 6.4 to 3.1 per hour, ensuring smoother operations during high-traffic periods. The system identifies points where SLM and LLM outputs align, allowing it to rely on more cost-effective local resources without compromising accuracy. Real-time guardrails quickly address non-compliant actions, keeping operations on track. As Anil Abraham Kuriakose from Algomox explains:
"AI-driven auto-scaling also minimizes the risk of downtime and enhances user experience by providing consistent and reliable service availability".
Additionally, multi-agent fault tolerance ensures continuous service delivery. If one specialized agent fails, others step in to maintain operations, even during unexpected demand surges.
5. Self-Healing Resource Optimization
Building on earlier models, self-healing resource optimization takes a proactive approach to maintaining consistent system performance. These systems are designed to autonomously detect and correct resource allocation issues. Using a telemetry layer, they monitor metrics like resource utilization, latency, throughput, and error rates across distributed clusters in real time. When issues arise - such as spikes in queue lengths or mismatches between local and cloud model outputs - automated feedback loops kick in. These loops handle tasks like redistributing workloads, reconfiguring resources, or breaking down failed subtasks into smaller units that can be rerouted to high-capacity cloud LLMs. This automation not only reduces costs but also enhances scalability and performance, as outlined below.
Cost Efficiency
Self-healing resource optimization delivers significant financial benefits. For instance, in April 2025, researchers at the University of Virginia and Microsoft introduced HERA (Hybrid Edge-cloud Resource Allocation), a lightweight scheduler for AI agents. HERA identified convergence points to offload 45.67% of subtasks to local Nvidia RTX 4090 GPUs, cutting operational costs by 30% and improving accuracy by 9.1% compared to older hybrid models. Beyond these immediate savings, self-healing systems actively reclaim wasted resources such as idle virtual machines, "zombie" servers, and unused software licenses, preventing overprovisioning and unnecessary cloud expenses. Analysis shows an average 169% return on investment over six months due to improved computational efficiency and lower infrastructure costs. Simbo AI highlights the broader impact:
"Automated monitoring and self-healing AI agents detect system health or security anomalies and automatically correct issues like restarting services or reallocating resources. This reduces unplanned outages, decreases revenue loss, and lowers support costs".
Scalability
These systems shine when it comes to scalability, dynamically adjusting resource allocation to meet real-time demand. AI-driven resource optimization has shown an average 31.2% increase in resource utilization, boosting efficiency from under 60% to over 91%. Predictive analytics enable the system to anticipate traffic spikes and scale capacity accordingly, distributing workloads across cloud, edge, and on-premises infrastructure to prevent bottlenecks. The complexity of coordinating interconnected AI agent subtasks requires advanced methods, as noted by Shiyi Liu and colleagues from the University of Virginia and Microsoft:
"The interconnected nature of agent subtasks requires a more sophisticated approach that considers both the individual subtask characteristics and their position in the overall reasoning chain".
This level of coordination ensures that optimizing one part of the system doesn’t inadvertently disrupt the whole.
Performance Optimization
Self-healing systems significantly improve throughput - by 38.7% - while also reducing energy consumption by 42.3%, thanks to real-time bottleneck mitigation. Techniques like "convergence detection" allow tasks to start on local SLMs and only switch to cloud LLMs if outputs begin to diverge, ensuring both high throughput and low latency. Additionally, priority-based reallocation algorithms with O(N) complexity enable rapid redistribution of GPU resources, adapting to workload intensity in milliseconds.
Resilience
The resilience of self-healing architectures is another key advantage. These systems are designed to recover from failures without requiring human intervention. As Matthew Finio from IBM Think explains:
"Fault tolerance is crucial and needs to be reinforced by designing failover mechanisms, redundancy strategies and self-healing architectures that allow the system to recover automatically without human intervention".
Predictive maintenance plays a critical role here. By analyzing logs and usage patterns, these systems can forecast hardware or software failures before they happen. Anil Abraham Kuriakose from Algomox elaborates on this proactive approach:
"AI-driven predictive maintenance uses machine learning models to analyze historical data and predict when components are likely to fail. This allows for timely maintenance and replacement, preventing unexpected outages".
In cases where issues do occur, self-healing systems employ "critic" agents to evaluate outputs against predefined standards. If results fall short, these agents trigger automated revision cycles. This approach minimizes deployment instability and ensures uninterrupted service, even during unexpected demand surges.
Comparison Table
When managing hybrid AI systems, each resource allocation model offers its own set of strengths. Knowing how these models compare can help you make informed choices tailored to your enterprise needs. Here's a breakdown summarizing key aspects like cost savings, scalability, performance, and resilience, based on research and real-world implementations in 2025.
| Model Type | Cost Savings | Scalability | Performance Optimization | Resilience |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reinforcement Learning-Based | Very High (30–77% savings) | High (handles dynamic environments) | Very High (70%+ makespan reduction) | Moderate (stable policy updates) |
| Predictive Analytics-Driven | High (prevents over-provisioning) | High (anticipates traffic spikes) | High (proactive adjustments) | Moderate (forecasts potential issues) |
| Autonomous Workload Distribution | Very High (45.67% offloading of subtasks) | High (edge-cloud synergy) | High (maintains accuracy within 2–5%) | High (modular isolation) |
| AI-Powered Auto-Scaling | Moderate-High (manages idle resources) | Excellent (dynamic resource adjustment) | High (real-time response) | High (failover capabilities) |
| Self-Healing Resource Optimization | Moderate (reduces repair costs) | Moderate | Moderate | Very High (automated recovery) |
Key Insights
- Reinforcement Learning-Based Models: These models, like ATSIA3C, deliver outstanding cost savings - up to 77.42% - while slashing execution times by over 70%. Their ability to adapt to dynamic environments makes them a top choice for performance-focused systems.
- Autonomous Workload Distribution: The HERA model exemplifies this category, achieving substantial monthly cost savings while keeping performance deviations within just 2–5% compared to cloud-only systems. Its edge-cloud synergy ensures scalability and high accuracy.
- Self-Healing Resource Optimization: This model shines in resilience, automatically detecting and fixing issues without human involvement. This ensures uninterrupted operation, making it a reliable choice for mission-critical systems.
Hybrid architectures that combine multiple AI and machine learning strategies consistently outperform single-method approaches across these metrics. Whether you're optimizing costs, enhancing scalability, or prioritizing resilience, the right model - or combination of models - can make a significant difference.
Conclusion
Hybrid AI resource allocation models can slash costs by 30% or more, all while maintaining accuracy levels within 2–5% of cloud-only configurations. For businesses handling 1 million requests, this translates to savings of $9,000–$26,000 per month.
But the benefits go beyond just cutting costs. These models tackle some of the biggest challenges enterprises face today, such as data sovereignty, security isolation, and real-time adaptability. The industry’s move toward multi-agent orchestration and edge-cloud hybrid setups highlights a growing awareness that monolithic, cloud-only systems often fall short in meeting modern AI needs. As Shiyi Liu from the University of Virginia explains:
"The interconnected nature of agent subtasks requires a more sophisticated approach that considers both the individual subtask characteristics and their position in the overall reasoning chain".
To implement these strategies effectively, businesses need a clear roadmap, robust orchestration patterns, and ongoing lifecycle management. NAITIVE AI Consulting Agency specializes in guiding organizations through this transformation. From readiness assessments to deploying hybrid schedulers like HERA - which intelligently divides subtasks between local and cloud resources - they ensure that adoption is seamless and avoids technical debt. Their tailored approach aligns each AI solution with your unique operational goals.
Whether you’re setting up an AI Center of Excellence, capping tokens to control costs, or building secure multi-agent systems, having the right partner can turn abstract potential into measurable outcomes. These proven strategies can help reframe AI as not just a cost but a strategic advantage.
FAQs
How do reinforcement learning-based models help reduce costs in hybrid AI systems?
Reinforcement learning-based allocation models are transforming how resources are managed by dynamically balancing tasks between local systems and the cloud. These models adjust hardware configurations on the fly to match demand, ensuring resources are used efficiently while avoiding over-provisioning and waste.
The benefits are clear: reduced cloud compute time, lower energy consumption, and trimmed operational expenses. In fact, research highlights energy savings of up to 42%, alongside considerable cost reductions. This makes these models an effective strategy for managing resources in hybrid AI setups.
What are the advantages of using predictive analytics for resource allocation in AI systems?
Predictive analytics enables AI systems to forecast demand, spot emerging trends, and allocate resources with greater precision. By tapping into data-driven insights, businesses can cut expenses, streamline operations, and make more informed choices.
This method ensures resources are directed to where they’re most needed, reducing waste and boosting overall system performance. It’s an effective way to fine-tune hybrid AI systems and drive improved results across a range of enterprise applications.
What is self-healing resource optimization, and how does it improve system resilience?
Self-healing resource optimization takes system management to the next level by actively monitoring the health of components like compute nodes, memory, and networks. When problems such as performance drops or failures arise, the system steps in automatically, reallocating workloads to keep things running smoothly and avoid downtime. A great example of this is how hybrid AI systems manage tasks. They can shift workloads between local small language models (SLMs) and cloud-based large language models (LLMs), ensuring both reliability and accuracy, even when disruptions occur.
In multi-agent setups, the game changes even more. Adaptive planners, driven by LLMs, can reassign tasks on the fly. Unlike static systems, these planners can cut latency by as much as 85%, offering businesses a way to maintain consistent performance, respond to sudden changes, and avoid resource bottlenecks. NAITIVE AI Consulting Agency is at the forefront of building these resilient AI frameworks, helping companies fine-tune their resources and boost the dependability of their AI systems.




