Real-Time Data Sync for Conversational AI
Keep conversational AI accurate and responsive with real-time sync using CDC, event-driven design, Kafka, and hybrid batch strategies.

Real-time data synchronization is essential for making conversational AI reliable and accurate. Without it, chatbots risk sharing outdated information, like showing incorrect inventory or missing critical updates. This can damage trust and lose customers.
Here’s what real-time sync does:
- Keeps AI systems updated with the latest data in seconds (e.g., inventory, user actions).
- Enables faster responses, like reducing lead response time from 12 hours to 90 seconds.
- Improves chatbot performance, boosting demo bookings by 34% in one quarter.
Key technologies include:
- Change Data Capture (CDC): Tracks database changes instantly.
- Event-Driven Architecture (EDA): Processes updates as they happen.
- Apache Kafka: Handles event streaming for scalable, reliable data flow.
Real-time sync is critical for dynamic tasks like fraud detection, live chat, and personalized user interactions. While batch sync is useful for large-scale, less frequent updates, combining both methods ensures efficiency and responsiveness.
NAITIVE AI Consulting Agency specializes in building these systems, ensuring chatbots work with the most current data, improving accuracy and user experience.
Designing Real-time Data Architectures patterns for AI Agents | Let's Talk About Data
Real-Time vs. Batch Synchronization
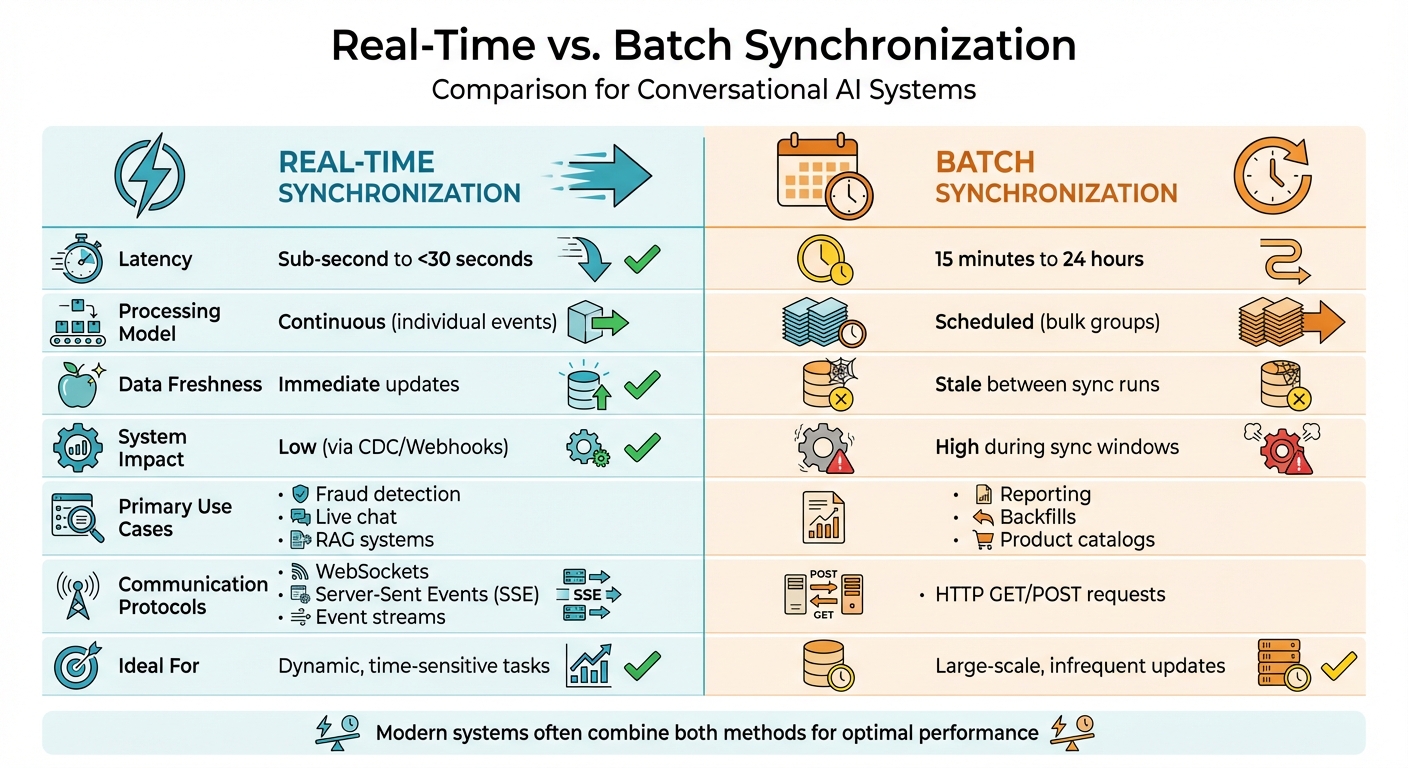
Real-Time vs Batch Data Synchronization Comparison for AI Systems
Understanding the distinction between real-time and batch synchronization is essential for ensuring conversational AI delivers timely and accurate responses. Real-time synchronization processes data as events occur - like when a user clicks "buy", the chatbot immediately recognizes the action. On the other hand, batch synchronization gathers data and updates it on a set schedule. The choice between these methods has a direct impact on user experience.
Technical Differences Between Real-Time and Batch Sync
The primary difference lies in how and when data is moved. Real-time synchronization works continuously, capturing changes in the database using technologies like Change Data Capture (CDC) and sending updates via webhooks or event streams. This method achieves latency of less than 30 seconds. Batch synchronization, however, processes data in bulk at scheduled intervals.
The communication protocols also vary. Real-time systems often use Server-Sent Events (SSE) for one-way streaming or WebSockets for two-way interactions. These are particularly effective for conversational AI, as SSE supports the token-by-token streaming required by large language models. Batch systems, in contrast, rely on HTTP GET/POST requests to transfer large data sets.
| Feature | Real-Time Synchronization | Batch Synchronization |
|---|---|---|
| Latency | Sub-second to <30 seconds | 15 minutes to 24 hours |
| Processing Model | Continuous (individual events) | Scheduled (bulk groups) |
| Data Freshness | Immediate updates | Stale between sync runs |
| System Impact | Low (via CDC/Webhooks) | High during sync windows |
| Primary Use Case | Fraud detection, live chat, RAG | Reporting, backfills, catalogs |
Real-time synchronization is more complex when it comes to managing state. For instance, simultaneous updates across devices require advanced conflict resolution, often using timestamp-based rules or three-way merges to determine the final state. Batch synchronization simplifies this by either overwriting data or appending it to logs.
These technical differences make real-time synchronization especially valuable for conversational AI applications.
Real-Time Sync Use Cases in Conversational AI
Fraud detection is one of the standout use cases for real-time synchronization. Banks and financial institutions can't afford delays when detecting suspicious activity. Real-time sync allows conversational AI to instantly access up-to-date transaction data, account balances, and risk assessments, enabling quick actions like blocking transactions or escalating issues within seconds.
Another example is creating adaptive conversation flows. Real-time updates allow chatbots to respond immediately to user actions, such as offering a discount when a customer abandons their cart. Without real-time data, these opportunities are often missed.
When Batch Synchronization Makes Sense
While real-time sync is ideal for immediate updates, batch synchronization shines in scenarios where delays are acceptable. For example, historical data analysis - like training AI models on months of customer interactions or preparing quarterly reports - doesn't require instant updates. Batch jobs can process large volumes of data during off-peak hours without straining live systems.
Batch sync is also well-suited for large-scale updates and reference data. For example, loading an entire product catalog or updating rarely changed user profiles is more cost-effective when done in bulk. Similarly, data that changes infrequently, like company policies or employee directories, can easily handle a 24-hour delay.
Modern systems increasingly combine both methods, often guided by specialized AI consulting to optimize architecture. Real-time synchronization handles high-frequency events like clicks, purchases, and chat messages, while batch synchronization manages stable data like catalogs and user profiles. This hybrid approach balances performance and cost, ensuring immediacy where needed and efficiency where possible.
Technologies That Enable Real-Time Data Sync
Real-time synchronization for conversational AI depends on advanced technologies designed to capture and deliver updates in milliseconds. This system uses a mix of approaches - such as event-driven architectures, database change capture, and event streaming - to ensure updates are instantly available to the AI platform.
Event-Driven Architectures
Event-driven architecture (EDA) treats every business action - like placing an order or updating a profile - as an event that triggers immediate action. Instead of waiting for scheduled processes, EDA sends these events to AI systems as they happen, allowing conversational AI to respond instantly.
"Event streaming is the digital equivalent of the human body's central nervous system... ensuring a continuous flow and interpretation of data so that the right information is at the right place, at the right time." - Apache Kafka Documentation
One major benefit of EDA is its flexibility. AI models, feature stores, and other components can subscribe to event streams independently without altering the main application. For example, if a new AI agent needs customer data, it simply subscribes to the relevant event topic. Additionally, EDA handles sudden traffic surges effectively - queuing messages during spikes and processing them as resources become available, which helps avoid system overload.
EDA also tackles the "stale knowledge" issue in Finetuning vs. RAG systems. When content in a CMS is updated, an event triggers immediate re-indexing in vector databases, ensuring chatbots reflect those updates within seconds, not hours.
Despite its advantages, EDA adoption varies. While 72% of organizations report using some form of event-driven architecture, only 13% describe their implementation as mature. Challenges like managing distributed event flows and ensuring strong error handling remain hurdles for many teams.
While EDA focuses on individual events, Change Data Capture (CDC) ensures that every database change is tracked in real time.
Change Data Capture (CDC) for Database Updates
Another critical piece of real-time sync is monitoring changes directly at the database level. Change Data Capture tracks every insert, update, and delete in primary databases, sending these updates to downstream systems without affecting performance. It often relies on log-based capture, which reads transaction logs (e.g., MySQL's binlog or PostgreSQL's Write-Ahead Log) to detect changes as they happen. Tools like Debezium and Striim convert these changes into event streams that can integrate with platforms like Apache Kafka.
For conversational AI, CDC ensures chatbots stay in sync with operational databases. For instance, when a customer service representative updates an order status, CDC instantly captures and relays this change to the AI system, ensuring users always receive accurate, up-to-date information.
Performance depends on the CDC method. Log-based CDC offers faster updates and minimal impact on source systems, whereas query-based CDC - which checks tables for timestamp changes - can miss deleted records and introduce delays.
Apache Kafka for Event Streaming

Apache Kafka plays a central role in real-time event streaming, offering a reliable and scalable way to move events between systems. Unlike traditional message queues that delete messages after delivery, Kafka stores events in partitioned logs, allowing multiple consumers to access them independently and repeatedly. This is especially useful for conversational AI workflows, where a single event stream might feed various components, such as real-time inference, personalization updates, or data storage for model retraining.
Kafka's fault-tolerant design ensures no data is lost during system failures, as events are replicated across multiple servers. For applications requiring audit trails or the ability to replay historical data, Kafka's persistent storage is invaluable.
Managed services like Confluent Cloud and AWS Kinesis simplify Kafka's setup and maintenance.
"Real-time AI works when models sit in the flow of events, not on top of nightly batches." - Valerie West, Head of AI & Automation, Launchcodex
When using Kafka for conversational AI, managing data formats is critical. A Schema Registry ensures that changes in producer data formats don’t disrupt downstream AI models, preventing system-wide failures.
Together, these technologies create a seamless framework for real-time data synchronization in conversational AI.
How to Implement Real-Time Data Sync
To ensure your AI remains responsive and accurate across devices, implementing real-time data sync involves leveraging event-driven architectures, Change Data Capture (CDC), and tools like Apache Kafka. However, the process also requires careful consideration of databases, conflict resolution strategies, and communication protocols.
Using Distributed Databases for State Management
Distributed databases replicate data across multiple nodes, maintaining consistency so conversational AI can access up-to-date information regardless of where the request originates. For transaction-critical data, distributed SQL databases like Tencent Cloud TDSQL-C and CockroachDB are ideal, as they ensure strong consistency. On the other hand, NoSQL solutions like Firebase Firestore and MongoDB Realm excel with their built-in sync listeners and offline-first capabilities.
If speed is your priority, in-memory stores like Redis Pub/Sub can deliver near-instant updates between microservices. For AI workflows involving Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), vector databases like Pinecone and Weaviate are essential, as they efficiently index high-dimensional context.
A practical example comes from Droptica, which, in November 2025, built a real-time RAG sync system for an AI-powered document chatbot. Their dual-layer setup, combining webhooks and nightly consistency checks, allowed updates to appear within 30 seconds across 11 content types. They managed 10,000–15,000 chunks with a 99.8% webhook success rate. When working with vector databases, it's best practice to delete old chunks before inserting new ones to prevent duplication and maintain clean state transitions.
Resolving Data Conflicts Across Multiple Devices
Conflicts can arise when users interact with AI systems on multiple devices simultaneously. To address this, solutions like Conflict-Free Replicated Data Types (CRDTs), Last-Write-Wins (LWW), and three-way merging offer effective ways to maintain data consistency.
- CRDTs provide automatic merging without needing a central coordinator. Apple Notes, for instance, uses CRDTs to handle offline edits, and League of Legends employs them for managing in-game chat with 7.5 million concurrent users.
- LWW is used by tools like Figma, which employs a server-authoritative approach for real-time collaboration. Figma also uses fractional indexing to maintain order in sequences.
- Three-way merging compares local, remote, and base states to resolve discrepancies.
"For AI systems, eventual consistency with intelligent conflict resolution often outperforms complex real-time protocols." - Gerred Dillon, Author, The Agentic Systems Series
For mobile apps, queuing operations during offline periods and syncing them later with CRDTs or version vectors ensures smooth functionality. Additionally, providing users with a clear sync status interface - indicating whether the system is active, offline, or resolving conflicts - can improve user experience.
Communication Protocols: WebSockets vs. HTTP Long Polling
Choosing the right communication protocol is critical for balancing response speed and network resilience.
- WebSockets create persistent, bidirectional connections with minimal latency, making them ideal for interactive chat. However, they can struggle with frequent disconnections and reconnection storms.
- HTTP Long Polling mimics real-time updates with moderate latency but is more robust in handling network interruptions due to its stateless nature.
- Server-Sent Events (SSE) are great for one-way streaming, especially for delivering LLM tokens, thanks to their built-in reconnection capabilities.
- For voice-based AI, WebRTC outperforms WebSockets in delivering media under unreliable network conditions.
- Adaptive polling adjusts polling frequency based on user activity and queue depth, reducing server load while staying responsive.
Teams using unified real-time infrastructure often achieve integration within five days. By aligning your protocol choice with your specific use case - whether it's WebSockets for chat, SSE for token streaming, or adaptive polling for unpredictable scenarios - you can seamlessly integrate these protocols into broader real-time sync systems. This ensures the accuracy and responsiveness required for event-driven architectures.
Best Practices for Real-Time Data Sync
To make your real-time data sync both efficient and secure, consider these practices that build upon the technologies we've explored.
Monitoring and Performance Tuning
Keep a close eye on critical metrics like end-to-end latency, sync coverage, and message throughput. For RAG systems, the latency - from when a data change occurs to when it’s reflected in your AI’s knowledge base - should stay under 30 seconds. Monitor synchronization coverage (the percentage of entity types syncing successfully) and message throughput to avoid issues like network congestion and CPU overload during high-frequency updates.
One example of a successful implementation achieved a webhook success rate of 99.8%, with trigger times under one second and re-indexing completed in 3-8 seconds. Combining real-time webhooks with nightly consistency checks can minimize overall latency while ensuring no updates are missed.
To optimize, use delta synchronization, which sends only the data that has changed, cutting down on bandwidth and reducing delays. Switching to binary protocols like Protocol Buffers or MessagePack instead of JSON can also help by lowering parsing overhead. Tools like Prometheus and Grafana can provide a multi-layer monitoring setup to track key metrics such as sync duration, transaction counts, and error rates. For stress testing, simulate thousands of concurrent connections using tools like k6 or Gatling to identify and resolve conflict scenarios.
"Latency is no longer just a delay, it's a competitive disadvantage. Stale data directly impacts business outcomes. AI models generate inaccurate predictions, customer-facing applications fail to deliver value, and fraud detection systems are rendered ineffective." - Striim Team
Data Security and Compliance Requirements
Security is crucial for protecting your AI system from vulnerabilities during data sync. Always enforce TLS encryption and reject non-HTTPS requests to secure connections. For webhook security, use HMAC-SHA256 signature verification to validate incoming events and prevent tampering. Additionally, implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and centralized secrets management for API keys and encryption tokens.
When handling sensitive data, align your security protocols with industry regulations. For example, healthcare systems must comply with HIPAA, while financial services often require SOC 2 and PCI DSS certifications. Maintain detailed audit logs of all sync operations to track data access and modifications. Keep encryption keys stored separately and rotate them regularly to meet compliance standards.
Scaling Event-Driven Architectures
As your AI system grows, your architecture must handle increased demands without sacrificing performance. Shard connections across multiple servers to avoid bottlenecks. Properly designed real-time APIs can support thousands - or even millions - of simultaneous connections. Using HTTP/2 or HTTP/3 multiplexing allows multiple message streams to run over fewer physical connections, which reduces resource usage.
Change Data Capture (CDC) is a great way to monitor transaction logs in real time without impacting production systems. Deploy edge servers, like Cloudflare Workers or AWS Lambda@Edge, to handle filtering and validation tasks closer to the end user, reducing the load on your core servers. Adaptive synchronization can also help by lowering update frequencies for inactive tabs or background sessions, cutting down on unnecessary processing. Finally, use platforms like Kubernetes for container orchestration to automatically scale resources based on CPU, memory, or custom metrics, and manage connections efficiently with idle timeout policies.
These strategies create a robust foundation for conversational AI systems, ensuring they deliver fast responses and maintain accurate data in real time.
Working with NAITIVE AI Consulting Agency
NAITIVE employs a dual-layer system that blends webhook-triggered re-indexing (with updates in under 30 seconds) and nightly consistency checks, achieving an impressive 99.8% webhook success rate. For the rare 0.2% of updates that slip through, nightly sync jobs step in to ensure no data is left behind. This setup ensures seamless data capture and integration across all NAITIVE implementations.
The agency utilizes Change Data Capture (CDC) to monitor transaction logs from systems like Oracle, SQL Server, and MongoDB without overloading production operations. CDC captures inserts, updates, and deletions in real time, delivering ultra-low latency. For organizations juggling over 500 distinct data sources in hybrid and multi-cloud setups, NAITIVE employs the Model Context Protocol (MCP). This open standard streamlines secure and standardized connections between AI models and enterprise data, slashing integration times from months to just 15–30 minutes.
NAITIVE's system builds on event streaming and CDC with modular endpoints tailored for real-time synchronization. These modular entity-specific endpoints are customized for different content types, helping isolate failures and optimize data chunking. For older systems lacking webhook support, NAITIVE mimics real-time notifications using internal polling. Additionally, technologies like Apache Kafka and DeltaStream power real-time processing of raw event streams - such as page views or cart updates - transforming them into actionable, high-value profiles for proactive AI agents.
Through its AI-as-a-Service (AIaaS) model, NAITIVE ensures low latency and balanced workloads, even under heavy demand, while maintaining data accuracy for conversational AI. The agency prioritizes establishing baseline performance metrics before implementation, then continuously tracks key indicators like response time variations, queue lengths, resource usage, and error recovery rates. This data-driven approach allows businesses to measure ROI by comparing pre- and post-implementation results in areas like customer acquisition and automated support.
NAITIVE also enforces a zero-trust architecture, verifying every data request through authentication, authorization, and auditing. By combining edge computing for time-critical tasks with cloud resources for scalable analytics, NAITIVE achieves rapid AI responses. Specialized hardware, including GPUs, TPUs, and NPUs, along with dynamic batching, further enhances responsiveness. These measures ensure the integrity and efficiency required for real-time conversational AI systems.
Conclusion
Real-time data synchronization takes conversational AI from being just a tool to becoming a powerful asset for businesses. When AI agents have access to live inventory, up-to-date order statuses, and the latest customer information, they can provide accurate and personalized responses. This not only boosts customer trust but also increases the chances of closing sales. The difference between a chatbot using outdated data and one operating in real time can literally mean the difference between losing a customer and gaining one.
Delays caused by outdated data can seriously harm customer trust, which is a significant risk in today's fast-paced business environment.
"In a world run on AI and instant analytics, stale data is a major business risk." - Striim Team
Technologies like Change Data Capture, Apache Kafka, WebSockets, and event-driven architectures address this issue by eliminating delays and ensuring data stays current. This enables businesses to engage proactively - for example, sending personalized offers immediately when a customer abandons their cart, rather than waiting hours for a batch process to catch up.
NAITIVE AI Consulting Agency specializes in implementing these capabilities with architectures designed to balance speed and reliability. Their solutions ensure that your conversational AI always works with the most current data, while maintaining the fault tolerance required for enterprise systems. The result? Better customer engagement and noticeable improvements in operational efficiency.
FAQs
How real-time does my chatbot need to be?
The speed at which your chatbot responds should align with its purpose and what users expect from it. For tasks that demand urgency - think customer support or voice assistants - responses need to be almost immediate. In dynamic fields like e-commerce or finance, quick reactions within milliseconds to a few seconds are essential to ensure reliability and maintain user trust. On the other hand, applications with less urgency can afford to take a bit more time, especially when handling complex processes.
What’s the easiest first step to add real-time sync?
Webhooks are a simple and effective way to integrate real-time sync into your system. With webhooks, external systems can send updates directly to your application as soon as changes occur. This eliminates the need for constant manual checks or delays in data updates. By setting up your backend to trigger notifications whenever there's a change in relevant data, your conversational AI can stay up-to-date and reflect the most current information seamlessly.
How do I keep data consistent across devices and outages?
Real-time data synchronization is crucial for keeping information consistent across devices, even during outages. To achieve this, you can rely on techniques such as change data capture (CDC), which tracks and applies data changes, and conflict-free replicated data types (CRDTs), which help resolve conflicts in distributed systems. Leveraging distributed architectures also plays a key role in ensuring data is updated across the network.
For low-latency updates, synchronization protocols like WebSocket or server-sent events (SSE) are ideal. Additionally, designing systems with an offline-first approach ensures that users can operate seamlessly without connectivity. Incorporating conflict resolution mechanisms allows the system to reconcile data and maintain consistency once the connection is restored.




