https://www.promptingguide.ai
Practical guide to prompt engineering: core techniques, CLEAR framework, tools (Langflow, OpenAI Agents), testing, evaluation, and production best practices.

Prompt engineering is the key to getting better results from AI models. It’s about crafting clear, structured inputs to guide AI in performing tasks like code generation, data analysis, or customer interaction. Without proper prompts, even advanced models like GPT-4.1 can fall short of their potential.
Here’s what you need to know:
- What it is: Prompt engineering involves creating precise instructions for AI to achieve specific outcomes.
- Why it matters: Better prompts save costs, improve accuracy, and unlock AI capabilities without expensive retraining.
- Techniques: Use methods like zero-shot (no examples), few-shot (with examples), or chain-of-thought (step-by-step reasoning) to tailor results.
- Resources: Visit https://www.promptingguide.ai for tools, tutorials, and courses on mastering this skill.
- Tools: Platforms like Langflow and OpenAI’s SDK simplify building workflows and multi-agent systems.
Start by structuring prompts using the CLEAR Framework (Context, Length, Examples, Audience, Role) for clarity and consistency. Test, refine, and monitor your prompts to ensure optimal performance over time. For business-critical tasks, pin models to specific versions to maintain stability.
Learn more and explore practical examples at https://www.promptingguide.ai.
The ADVANCED 2025 Guide to Prompt Engineering - Master the Perfect Prompt...
Core Prompting Techniques
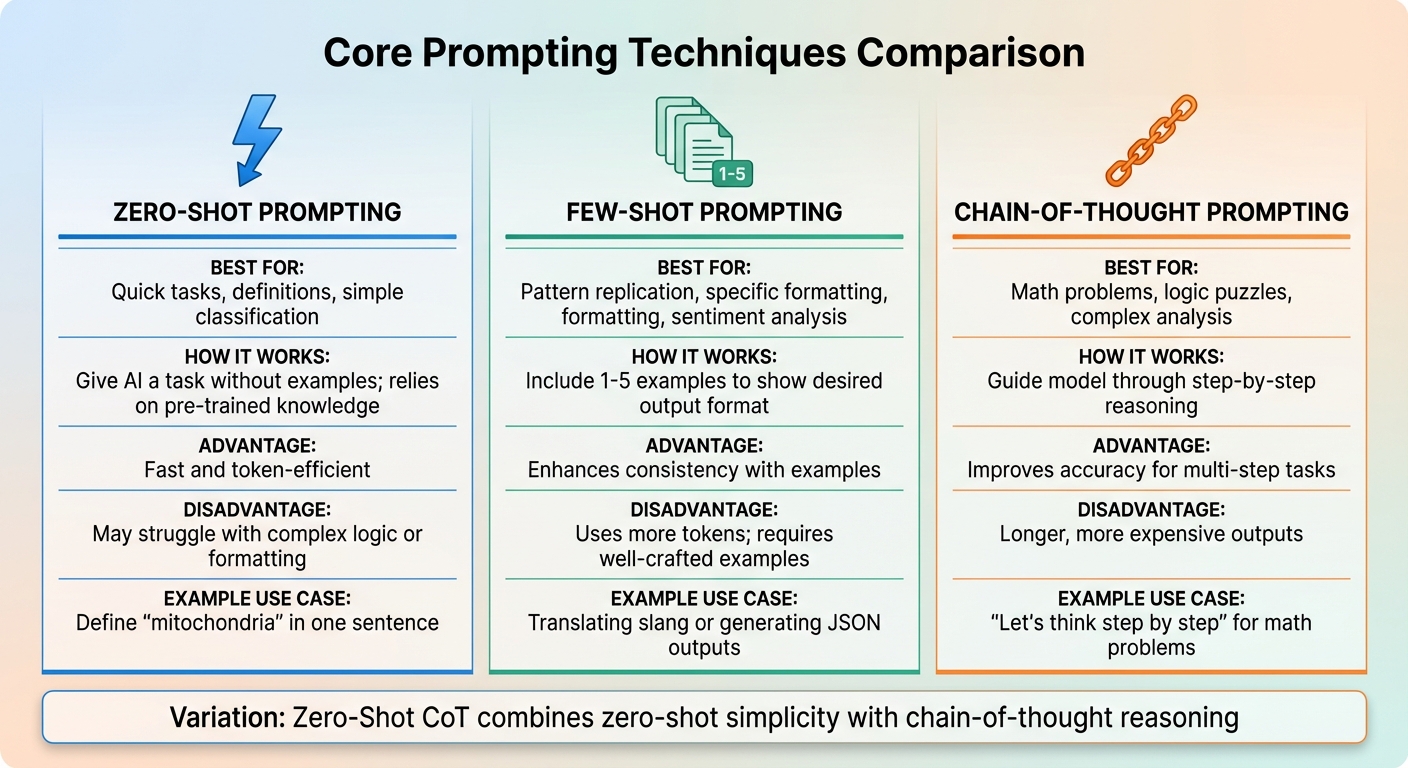
Core AI Prompting Techniques Comparison: Zero-Shot vs Few-Shot vs Chain-of-Thought
This section dives into three essential techniques to get the most out of AI models: zero-shot, few-shot, and chain-of-thought prompting. Each method has its strengths, and understanding when to use them can make a big difference in your results. Let’s break down each approach so you can choose the best one for your needs.
Zero-Shot Prompting
Zero-shot prompting is as simple as it gets: you give the AI a task without offering any examples. The model relies entirely on its pre-trained knowledge to provide an answer. This method is great for straightforward tasks like defining terms, basic summarization, or simple classifications. For example, you might ask, "Define 'mitochondria' in one sentence."
The main perk here is efficiency. Zero-shot prompts are quick and use fewer tokens, making them perfect for uncomplicated questions. But when the task involves complex logic, specific formatting, or niche topics, this approach can fall short. Without examples, the AI may misinterpret your request, leading to uneven or incorrect results.
"Prompt engineering is simply the art and science of crafting effective instructions for AI tools. Think of it like learning to give clear directions to a very capable but literal-minded assistant." - Prompts & Tools
For simple tasks, start with zero-shot prompting. Add complexity only when the situation demands it.
Few-Shot and One-Shot Prompting
Few-shot prompting takes things up a notch by including a handful of examples - usually one to five - to show the AI what you're looking for. This technique taps into in-context learning, where the model picks up on patterns and formats just by observing your examples. One-shot prompting is a variation that uses just one example.
This method shines when you need the AI to replicate specific styles or structures. For instance, translating slang or generating JSON outputs benefits from a few examples to establish the tone or format. It’s also useful for sentiment analysis or tasks that require consistent formatting.
The downside? Few-shot prompts use more tokens, which can increase costs. Plus, the examples need to be well-thought-out to guide the AI effectively. When executed properly, though, this technique can deliver reliable results for tasks that might otherwise require more extensive fine-tuning.
Chain-of-Thought Prompting
Chain-of-thought (CoT) prompting is all about step-by-step reasoning. Instead of asking for a direct answer, you guide the model to break down the problem into smaller steps. This is especially helpful for tasks like math problems, logic puzzles, or situations that require detailed analysis.
For example, instead of asking, "If Jessica has 12 apples, gives away 5, and buys 8, how many does she have?", you’d say, "Let’s think step by step." This encourages the model to process the problem sequentially, which can significantly improve accuracy for multi-step tasks.
One variation, zero-shot CoT, combines the simplicity of zero-shot prompting with the reasoning power of chain-of-thought. By adding a phrase like "Let’s think step by step" to a zero-shot prompt, you can trigger the AI’s reasoning capabilities without needing to provide examples.
The trade-off? CoT prompts tend to produce longer outputs, which can take more time and increase costs.
| Technique | Best For | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zero-Shot | Quick tasks, definitions, simple classification | Fast and token-efficient | May struggle with complex logic or formatting |
| Few-Shot | Pattern replication, specific formatting, sentiment analysis | Enhances consistency with examples | Uses more tokens; requires well-crafted examples |
| Chain-of-Thought | Math problems, logic puzzles, complex analysis | Improves accuracy for multi-step tasks | Longer, more expensive outputs |
These foundational techniques set the stage for more advanced methods, which we’ll explore in the next section to help you refine your AI prompts even further.
Advanced Methods and Best Practices
Once you've mastered the basics of prompting, it's time to level up. These advanced techniques can make a huge difference, transforming your results from "okay" to consistently effective. The secret? It's all about how you structure, test, and refine your prompts while steering clear of common mistakes. Whether you're building workflows or just trying to get better responses, these methods help ensure precision and control.
How to Structure Prompts for Clarity
A well-structured prompt is like giving clear instructions to a teammate - it sets expectations and minimizes confusion. The CLEAR Framework is a handy tool to organize your prompts effectively:
- Context: Set the scene or provide background.
- Length: Specify how detailed or brief the response should be.
- Examples: Share sample outputs to guide the AI.
- Audience: Define who the response is for.
- Role: Assign a persona or perspective for the AI to adopt.
For example, instead of saying, "Help me with a report", try this: "Write a 500-word executive summary for a Q4 sales report targeting C-suite executives." This level of detail leaves no room for ambiguity and leads to sharper results.
Another great tip? Use Markdown headers or XML tags to create clear boundaries in your prompts. For instance, wrap user input in <user_query> tags or supporting materials in <context> tags. This helps the AI separate instructions from data. OpenAI also suggests assigning roles like developer, user, or assistant to clarify priorities and guide behavior.
Want even more control? Add negative instructions. For instance, specify, "Do not use emojis or casual slang." These small tweaks ensure the output aligns with your vision.
Once the prompt is structured, it's time to test and refine it.
Testing and Refining Prompts
Perfecting a prompt isn't a one-and-done process. Start with a simple version, test the output, and build from there. If the results feel generic, add more context, examples, or tone specifications - like asking for a "conversational but professional" style.
If you're using prompts in production, set up evaluations to monitor performance over time. These checkpoints help you catch unexpected changes, especially when models are updated. A good practice here is model pinning - locking your application to a specific version (e.g., gpt-4.1-2025-04-14). This ensures consistency, which is vital for business-critical tasks.
For complex requests, break them into smaller steps. Instead of asking, "Create a marketing plan", split it into parts like "Identify target demographics", "Draft three campaign ideas", and "Estimate budget requirements." This approach makes it easier for the AI to deliver accurate and actionable results.
And don't forget - refining your process means learning from your mistakes.
Common Prompting Mistakes to Avoid
Even the most experienced users can slip up. Here are some common pitfalls and how to sidestep them:
- Information Overload: Overloading the AI with unnecessary details can confuse it and weaken the response. Stick to the essentials.
- Ignoring Bias: AI models often lean toward common patterns or assumptions. If precision matters, provide clear examples or descriptions to guide the output.
- Treating Prompts as Final: Don’t settle for the first result. Review and tweak your prompts to improve the outcome. For instance, if the tone feels off, ask for changes like "Make this more formal" or "Add a section on risks."
- No Output Format: Assuming the AI will guess the format you want is a recipe for frustration. Always specify the structure - like JSON, bullet points, or a specific word count - to avoid wasting time on manual reformatting.
| Mistake | Why It Happens | How to Fix It |
|---|---|---|
| Information Overload | Including too much irrelevant context | Focus only on critical information |
| Ignoring Bias | Overlooking model tendencies | Use explicit examples or descriptions |
| Treating Prompts as Final | Failing to iterate based on results | Refine prompts after initial review |
| No Output Format | Assuming the AI will infer structure | Specify formats like JSON or bullets |
"Rather than a rigid technical skill, prompt engineering is more about mastering the art of communicating with AI to achieve consistent, controllable, and repeatable results." – Casimir Rajnerowicz, Content Creator, V7 Labs
Tools and Frameworks for Prompt Engineering
When advanced prompting techniques meet the right tools, the process becomes much more streamlined. These tools transform prompt engineering into a structured approach, helping to build interactive workflows, automate tasks, and deploy reliable systems.
Langflow for Interactive Prompt Design
Langflow is an open-source Python framework that simplifies the creation of applications like chatbots and document analyzers by offering a visual, drag-and-drop interface. Instead of coding from scratch, you design "flows" using nodes, each representing a specific task - like connecting to a data source, serving an AI model, or processing text. The framework’s interactive "Playground" feature lets you test components in real time, ensuring everything works as intended before finalizing your flow.
Once you’ve refined your design, Langflow’s API allows you to embed these flows directly into your applications. You can also save and share flows, making it easy to version and distribute them across teams. It supports custom Python components and integrates seamlessly with the Model Context Protocol (MCP).
To get started quickly, Langflow offers pre-built templates such as "Basic Prompting" or "Vector Store RAG." These templates help you hit the ground running while also enabling you to isolate and test individual components to catch issues early.
OpenAI Agents SDK for Automation
The OpenAI Agents SDK simplifies automation by managing a repeating agent cycle that handles tasks like calling tools, processing results, and iterating until completion. Built with Python, the SDK uses familiar constructs like loops, conditionals, and functions to chain agents and define workflows. Any Python function can be turned into a tool with automatic schema generation and validation, making integration with external APIs straightforward.
For more complex workflows, the SDK includes a Handoff feature, allowing specialized agents to collaborate. For example, a "Triage Agent" can delegate tasks to a "CRM Agent" for more specific handling. Safety guardrails ensure inputs and outputs are validated, halting processes when something goes wrong. The system also manages conversation history automatically, saving you from manual context handling. Integrated tracing tools let you visualize agent logic, tool usage, and reasoning steps in real time.
"The OpenAI Agents SDK aims to be a conceptual framework demonstrating how different agents, such as a 'Triage Agent' or a 'CRM Agent,' can collaborate to complete tasks via tool interactions and delegation mechanisms." – Anna, Technical Writer at CometAPI
In March 2025, Coinbase used the OpenAI Agents SDK to prototype and deploy multi-agent support systems, which led to faster rollouts and more reliable customer interactions. By using specialized agents instead of a single, all-encompassing prompt, they achieved better task delegation and system reliability. Implementing guardrails early and leveraging tracing tools helped identify bottlenecks and improve overall efficiency.
These tools not only automate complex workflows but also prepare organizations for seamless AI integration, setting the stage for tailored solutions like those offered by NAITIVE AI Consulting Agency.
NAITIVE AI Consulting Agency's Approach
NAITIVE AI Consulting Agency specializes in designing AI solutions that deliver measurable results. By incorporating tools like Langflow and the OpenAI Agents SDK, the agency focuses on creating tailored systems that align with your business needs.
Their process starts with a detailed evaluation of your organization to identify areas where AI can enhance operations. Whether it’s automating up to 80% of your SEO content creation or implementing multi-agent systems for customer service, every solution is designed to improve efficiency and consistency.
From concept to implementation, NAITIVE AI guides businesses in unlocking the full potential of AI to streamline operations and achieve tangible outcomes.
Evaluating and Optimizing Prompts
How to Measure Prompt Performance
Start by defining what success looks like for your prompts. Common criteria include accuracy, factuality, relevance, and alignment with the intended task. To track efficiency, monitor metrics like token usage, response time, and cost per 1,000 tokens.
The way you evaluate prompts depends on the task at hand. For translation or summarization, metrics like BLEU and ROUGE are widely used. When it comes to reasoning or tone, the "LLM-as-Judge" method leverages models like GPT-4 to assess outputs on a larger scale. However, for subjective qualities like creativity, human evaluation remains the most reliable approach.
"Prompt engineering without evaluation is guesswork." – Maxim AI
If your goal is accuracy - like in research tools - recommended settings include a temperature of 0.1, top-p of 0.9, and top-k of 20. On the other hand, creative tasks benefit from a temperature of 0.9, top-p of 0.99, and top-k of 40. These settings provide a foundation for prompt tuning, a key focus in optimizing performance.
After measuring performance, shift your attention to reducing bias and ensuring consistent results.
Reducing Bias and Ensuring Consistency
One way to test for stability is by paraphrasing your prompts and checking if the outputs remain consistent. To prevent issues like toxic responses or guideline violations, use safety tools such as the Moderation API. For systems that rely on retrieval-augmented generation, faithfulness metrics help ensure the model sticks to the provided source material without inventing facts.
Incorporating guardrails directly into your prompts can proactively address potential problems. For example, you can include instructions on when the AI should decline a request, how to handle low-confidence outputs, or how to respond to ambiguous queries. Regular monitoring of production environments is also critical to detect and address any performance drift over time.
Once biases are minimized and consistency is achieved, the next step is to refine prompts for use with new AI models.
Updating Prompts for New AI Models
Adapting prompts to new AI models is a natural progression after evaluation and bias reduction. Treat your prompts like code - track versions alongside evaluation scores to monitor improvements. Use model pinning to lock production applications to specific snapshots (e.g., gpt-4.1-2025-04-14), ensuring stability even when providers roll out updates. This approach lets you test newer models in isolated environments before deploying them in production.
Different models often require different strategies. For example, reasoning-focused models like GPT-5 or o-series excel with high-level goals, while standard GPT models perform better with step-by-step instructions. Start by testing a zero-shot baseline and a few-shot variant, then compare their outputs and costs across two or three models before making a final decision. Including static content, such as instructions, at the beginning of your prompts can also reduce costs by taking advantage of prompt caching.
A/B testing in live environments is another effective way to see how prompt variations impact real user behavior. This process can uncover edge cases that controlled testing might overlook. Finally, integrating prompt evaluation into automated testing pipelines ensures new versions meet quality standards before they go live, maintaining consistent performance with every release.
Conclusion
Prompt engineering has the power to elevate AI performance from ordinary to outstanding. The website https://www.promptingguide.ai serves as a solid starting point for anyone looking to master this skill. It covers everything from simple Zero-Shot techniques to advanced strategies like Chain-of-Thought and ReAct, offering a well-rounded foundation for learners. With over 3 million users and widespread adoption among Fortune 500 companies, this platform has proven its practicality in real-world scenarios.
A great place to begin is with the CLEAR Framework, which helps structure prompts effectively. You can test these approaches using the Python notebooks available on the site. For tasks requiring complex reasoning, a simple addition like "Let's think step by step" can significantly enhance accuracy. As JD Meier aptly said, "Prompting isn't about asking better questions. It's about creating better patterns".
To tackle advanced AI tasks, evolving your prompt strategies is crucial. As AI shifts toward agentic systems, prompts need to go beyond basic text generation. Tools such as Langflow, Flowise, and the OpenAI Agents SDK can help you build multi-agent systems capable of planning, executing, and adapting. For consistency in production, pin your applications to specific model snapshots (e.g., gpt-4.1-2025-04-14) and use evaluation pipelines to assess performance before making updates. These practices highlight the core takeaway: effective prompt engineering is essential for unlocking AI's full potential.
To take your skills further, don't miss out on the 20% discount for advanced courses by using the promo codes AGENTX20 or PROMPTING20. These courses are designed to refine your ability to build AI workflows and agents. Transition from vague prompting to a more rigorous, data-driven approach - track your versions, measure outcomes, and refine continuously.
Finally, head over to https://www.promptingguide.ai, explore the Examples section, and experiment with prompts in the OpenAI Playground. The difference between AI that underwhelms and AI that excels often lies in how thoughtfully its prompts are engineered.
FAQs
What are the advantages of using the CLEAR Framework in prompt engineering?
The CLEAR Framework offers a straightforward way to craft effective prompts by focusing on five key elements: Context, Length, Examples, Audience, and Role. This approach ensures prompts are well-structured, easy to understand, and specifically designed to meet the AI's requirements, reducing confusion and improving the relevance of responses.
By addressing these elements, the framework helps create a standardized method for prompt writing. This makes it easier to adapt and reuse prompts across different projects. It also tackles common problems like prompts that are too vague or excessively long, leading to quicker iterations and more consistent outcomes. In short, CLEAR streamlines the process of working with AI, making interactions more efficient, accurate, and reliable.
What’s the difference between zero-shot and few-shot prompting?
Zero-shot prompting means assigning a task to the AI without offering any examples. Instead of examples, the prompt consists of clear instructions or a description of what the output should look like. The AI then generates a response based solely on its pre-trained knowledge.
In contrast, few-shot prompting provides the AI with a handful of examples (usually 1–5) that illustrate the task at hand. These examples give the model a sense of the pattern or context, which it uses to handle new inputs. Essentially, this method serves as a quick way to guide the AI by demonstrating the expected response before posing the actual question.
Both techniques play an important role in prompt engineering, and the choice between them depends on how much direction the AI needs for the task.
What tools can simplify and enhance prompt engineering?
Several tools can help make prompt engineering simpler and more effective. Take OpenAI’s Agents SDK, for instance. It automates tasks like managing context, refining prompts, and integrating tools. This means you can develop and scale AI-powered applications without diving into complex coding.
Another resource, the Prompting Guide, includes features like the Automatic Prompt Engineer (APE), which tailors and optimizes prompt variations to align with your objectives. It also incorporates the ReAct framework, which blends logical reasoning with tool usage seamlessly.
These tools are designed to streamline the entire workflow - from crafting and testing prompts to deploying them - allowing you to achieve higher-quality results with less effort.




