AI Agents in Urban Planning: Case Studies
Case studies on AI agents optimizing traffic, site analysis, energy use, environmental monitoring, and community engagement in urban planning.

AI is transforming urban planning by making cities smarter, faster, and more efficient. From traffic management to energy optimization, these systems are solving complex urban challenges. Here’s what you need to know:
- Traffic Optimization: Cities like Tucson and Chattanooga have reduced delays by up to 57% and cut emissions using AI-powered systems.
- Site Analysis: Tools like SiteSolve now complete in minutes what used to take months, streamlining urban development.
- Resource Management: AI forecasts housing and energy needs with precision, helping cities prepare for rapid growth.
- Environmental Monitoring: AI identifies heat islands and manages carbon footprints, aiding climate resilience efforts.
- Community Engagement: AI simulates resident feedback and visualizes proposals, making urban planning more inclusive.
AI is no longer just a tool - it’s reshaping how cities function and grow, addressing today’s urban challenges with data-driven solutions.
AI Impact on Urban Planning: Key Performance Metrics Across Global Cities
Traffic Management and Urban Mobility
Real-Time Traffic Optimization
Traffic congestion is a persistent challenge for cities worldwide, but AI is stepping in to make a difference. Instead of relying on outdated fixed-timing traffic signals, cities are adopting adaptive systems powered by AI. These systems use sensor data and historical trends to adjust traffic signals dynamically, reducing delays and improving safety for everyone on the road.
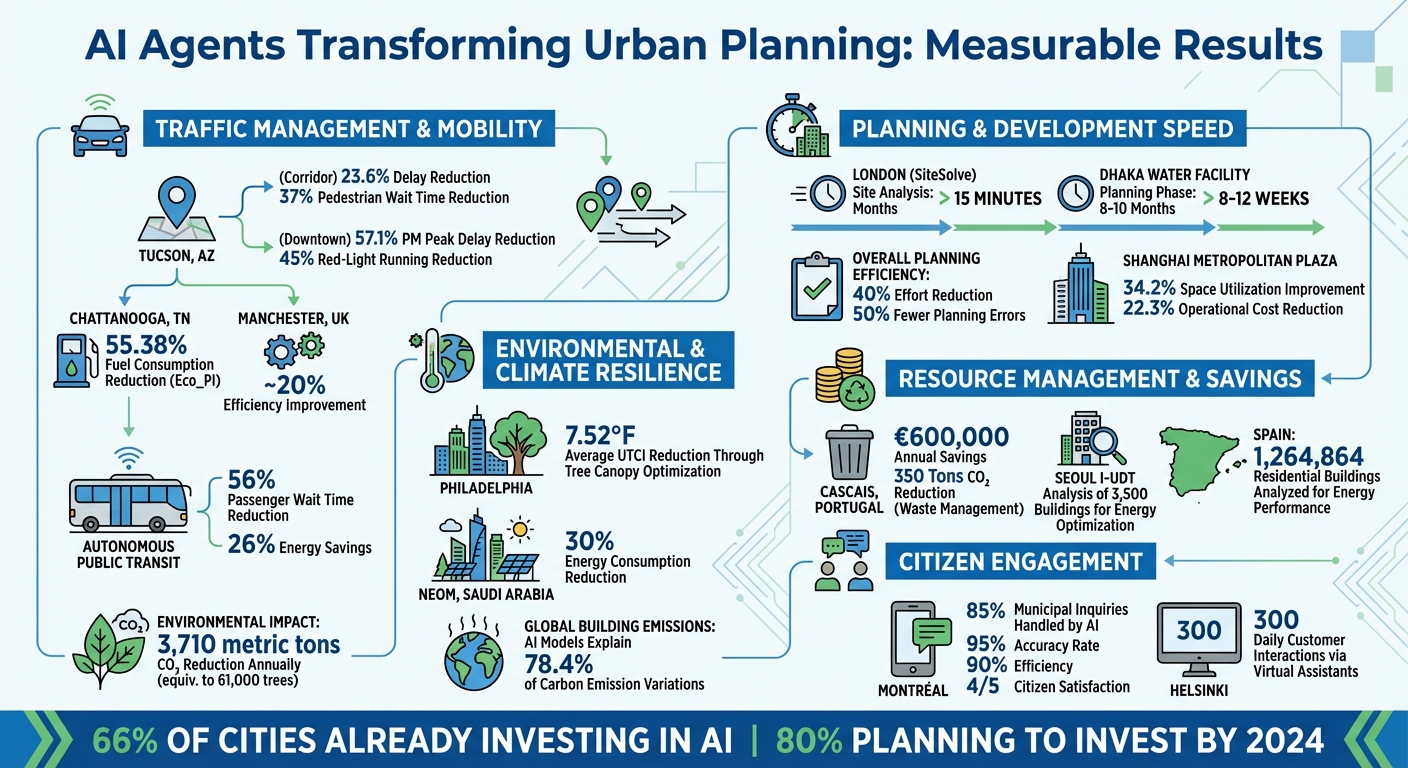
Take Tucson, Arizona, for example. In February 2025, the city teamed up with NoTraffic to implement an AI Mobility Platform along key corridors like Campbell Avenue and Broadway Boulevard. The results were impressive: delays dropped by 23.6% overall, with morning peak delays down by 20.7% and evening peak delays reduced by 18.4%. Pedestrians benefited too, with wait times near the University of Arizona slashed by 37%. Plus, the environment got a boost - annual CO₂ emissions fell by 3,710 metric tons, which is equivalent to planting 61,000 trees.
Downtown Tucson saw even more dramatic results. AI optimization cut control delays by 48.5% and evening peak delays by a whopping 57.1%. Pedestrian delays in some areas were reduced by up to 80%, and incidents of red-light running dropped by 45%. The system also tackled gridlock issues like spillback and blocked left turns, making traffic flow much smoother.
Another example comes from Chattanooga, Tennessee. In April 2024, researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory introduced a cutting-edge approach on the Martin Luther King (MLK) Smart Corridor. Using Decentralized Graph-Based Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (DGMARL) paired with a Digital Twin, each intersection acted as its own independent agent, learning and adapting to local traffic patterns. The outcome? A 55.38% reduction in Eco_PI - a measure of fuel consumption and stop delays - over a full day, with a 38.94% drop during evening peak hours.
Across the pond, Transport for Greater Manchester tackled complex traffic scenarios with the "SimplyfAI" project in January 2019. By processing enriched traffic data, their AI planning agent created real-time signal strategies for managing events like road closures and saturated intersections. Simulations showed a roughly 20% improvement in efficiency.
These examples show how AI doesn't just optimize traffic signals - it’s reshaping how cities manage urban mobility.
Autonomous Routing Systems
AI isn't stopping at traffic lights. It's also transforming vehicle routing and public transit systems. Using Spatio-temporal Graph Neural Networks, AI models urban transport systems as dynamic graphs, enabling real-time routing that balances efficiency, energy use, and fairness.
Autonomous Public Transport Systems (APTS) powered by AI are making a big impact. These systems adapt to passenger demand instead of sticking to rigid schedules. The result? Average wait times for passengers drop by 56%, and energy use is cut by 26%. This flexibility makes public transit more responsive and efficient.
The same DGMARL technology used for traffic signals is now being applied to route planning for autonomous vehicles. By treating roads as interconnected graphs, AI calculates optimal routes that reduce congestion, save fuel, and promote equitable service distribution. Modern routing frameworks are even incorporating equity measures - like the Theil Index - to ensure that efficiency doesn’t come at the expense of fairness.
Here’s a quick look at some key improvements:
| Location | Implementation | Metric | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tucson, AZ (Corridor) | NoTraffic AI Platform | Overall Delay Reduction | 23.6% |
| Tucson, AZ (Downtown) | NoTraffic AI Platform | PM Peak Delay Reduction | 57.1% |
| Chattanooga, TN | DGMARL + Digital Twin | Fuel Consumption (Eco_PI) | 55.38% |
| Manchester, UK | SimplyfAI Planning Agent | Efficiency Gain (Simulation) | ~20% |
| APTS Implementations | AI-Driven Routing | Passenger Wait Times | 56% |
Building Smart Cities With Digital Twins and Agentic AI
Site Analysis and Development Feasibility
Urban development has long been bogged down by the slow, manual process of compiling data for feasibility studies. These efforts often stretch over months, delaying progress. But with AI stepping in, cities are now cutting planning time dramatically. What used to take weeks of consultant labor can now be accomplished in mere minutes.
Take the London Borough of Haringey, for example. In December 2025, planners utilized SiteSolve, a generative AI tool integrated with VU.CITY's platform, to assess potential development sites. Within just 15 minutes, the system generated 3D massing models that accounted for daylight requirements, amenity spaces, and local policy constraints. This rapid turnaround is reshaping how urban designs are approached, paving the way for faster, smarter planning.
Generative Design in Urban Planning
AI isn’t just speeding up site analysis; it’s revolutionizing the way entire neighborhoods are designed. By evaluating hundreds of development scenarios simultaneously, AI tools can test multiple options against zoning regulations and other criteria in record time.
A striking example comes from July 2024, when the Dhaka Water Supply and Sewerage Authority teamed up with the Asian Development Bank to use the Transcend Design Generator for a water treatment facility. This AI tool optimized the facility’s layout and operations, slashing the planning phase from a lengthy 8–10 months down to just 8–12 weeks.
In another case, researchers in Seoul created an Intelligent Urban Digital Twin (I-UDT) in February 2025. Using GPT-based AI agents, they analyzed 3,500 buildings across the city. The system automatically combined fragmented administrative records with energy consumption data, performing tasks like feature engineering and predictive modeling - processes that would have required an enormous manual effort. As the research highlighted:
The GPT automatically integrates and analyzes data and information collected from the real world, enabling it to serve as the virtual model of the DT [Digital Twin].
Time-Saving Feasibility Assessments
By blending generative design with feasibility assessments, AI is streamlining urban planning workflows like never before. A report from Oliver Wyman revealed that applying AI in planning processes can reduce overall effort by 40% while cutting planning errors in half.
One example comes from Shanghai’s Metropolitan Central Plaza, where an AI-driven responsive design framework boosted space utilization efficiency by 34.2% and reduced operational costs by 22.3% compared to traditional static design methods.
Similarly, the Yarra Ranges Shire Council in Victoria, Australia, faced delays due to complex regulations and limited staffing. Between August 2023 and June 2024, they partnered with MyLot to develop a generative AI tool funded by a $300,000 Digital Planning Grant. The MyLot Digital Planning tool significantly shortened application timelines, allowing staff to focus on more intricate cases.
Predictive Infrastructure Planning and Resource Optimization
Urban areas are growing rapidly, and cities need to plan their infrastructure to keep up with this shift. With 68% of the world's population expected to live in urban areas by 2050, it's clear that cities must anticipate future needs with precision. AI is stepping in to handle this challenge, forecasting demands and allocating resources in ways that go beyond what manual methods can achieve. From predicting population growth to managing energy systems, AI is reshaping how cities prepare for the future.
Forecasting Population Growth and Housing Needs
Predicting where people will live and how much housing they’ll need is no simple task. It involves juggling factors like income, employment, and financing. AI, with its ability to process and analyze complex data, is proving to be a game-changer in this area.
Take the example of Deloitte’s "Intuition" time series accelerator, introduced in February 2022 for a city planning department within the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC). This system automated the identification of trends across residential and industrial sectors, allowing stakeholders to model various scenarios for housing demand. By layering data such as household income, pricing, rents, and district-specific occupancy rates, the AI delivered a detailed supply-demand analysis in just days - something that would have taken months using traditional methods.
In another instance, Newcastle City Council partnered with the Alan Turing Institute in 2024 to use neural networks for modeling land use impacts. This AI system evaluated how specific planning decisions could influence house prices and job accessibility. It then proposed optimal land use strategies to help meet policy goals, addressing both current and long-term needs.
But AI’s role doesn’t stop at housing. It’s also making strides in optimizing energy and utility systems, which are critical for sustainable urban development.
Energy and Utility Resource Management
Managing energy efficiently is essential for building sustainable cities, and AI is revolutionizing how planners optimize energy grids and utilities.
A notable example comes from Seoul, South Korea, where researchers at Sungkyunkwan University’s Building Information Science & Technology Lab implemented an Intelligent Urban Digital Twin (I-UDT) in February 2025. This system, powered by GPT-4, integrated fragmented data from 3,500 buildings to predict energy consumption and assess sustainability benchmarks. According to MDPI Smart Cities (2025):
"Implementing I-UDTs enables urban policymakers to make data-driven decisions, improve energy efficiency, and enhance the scalability of digital twin applications."
On a larger scale, Spain adopted a nationwide Urban Building Energy Modeling approach in 2021. Led by Velamazán, the project used XGBoost and other AI tools to analyze energy consumption across 1,264,864 residential buildings. The system categorized these buildings into energy performance grades (A to G), creating a foundation for Spain’s carbon-neutral strategies.
In Sweden, researchers in Varberg took a similar approach in 2020. Using AI-driven simulations, they studied how large-scale energy retrofits on 22,000 residential buildings would affect electricity demand and grid stability. By analyzing Energy Performance Certificate data, the team provided critical insights for utility infrastructure planning.
These examples highlight how AI is not just forecasting future needs but also enabling smarter, more efficient resource management to support sustainable urban growth.
Environmental Monitoring and Climate Resilience
Cities are feeling the brunt of climate change. Urban heat islands, for instance, can cause warming rates to double, and heat-related deaths among people aged 65 and older surged by about 85% between 2017 and 2021. To tackle these challenges, cities need tools that can predict threats and enable quick responses. This is where AI steps in, processing environmental data far quicker than traditional methods.
Urban Heat Island Analysis
Tracking urban heat islands requires sifting through massive amounts of data from satellites, weather reports, and city infrastructure. AI makes this process seamless by combining these diverse data sources to pinpoint heat hotspots with incredible precision.
Between 2020 and 2022, the City of Calgary used a tool called "AI for the Resilient City", developed by Evergreen with support from Microsoft AI for Earth. By analyzing satellite images and 3D city models, the system identified urban heat island hotspots across Calgary. This data influenced five planning projects and 10 public infrastructure initiatives, resulting in "Community Climate Risk Profiles." These profiles now guide decisions on preserving natural cooling assets like green spaces.
Columbus, Georgia, adopted a different strategy in August 2022 by introducing a Smart City Digital Twin at key intersections in the city. Using YOLOv3 and DeepSORT computer vision algorithms paired with meteorological sensors, the system monitored a composite heat index. During a public event, the AI detected a sharp rise in heat stress as more than 1,000 pedestrians passed through in just four hours. This data enabled emergency cooling measures to be deployed proactively.
Philadelphia researchers took another step forward in July 2025, applying the GSM-UTCI multimodal AI framework to simulate changes across 104.5 square miles of the city. Their findings revealed that replacing impervious surfaces with tree canopies could lower the Universal Thermal Climate Index (UTCI) by an average of 7.52°F. Thanks to the model’s hyperlocal, 1-meter resolution predictions, urban planners can now focus interventions where they’ll make the most difference.
These temperature insights are also crucial for shaping broader urban strategies around carbon emissions.
Carbon Budgeting and Emissions Management
To manage carbon emissions effectively, cities need a clear picture of how energy is consumed across thousands of buildings and where reductions will have the most impact. AI now integrates data on building energy use, consumption patterns, and geographic details to generate detailed, city-wide carbon footprints.
Seoul’s Intelligent Urban Digital Twin (I-UDT) is a prime example. By combining fragmented administrative data, the system predicts energy consumption and evaluates buildings against carbon-neutral benchmarks, enabling informed urban policy decisions.
NEOM, Saudi Arabia, has pushed this concept further as part of its Vision 2030 initiative. Using deep learning and reinforcement learning algorithms, along with a network of IoT devices and weather stations, NEOM’s AI-driven system has cut energy consumption by 30%, advancing its goal of building a carbon-neutral urban ecosystem. A 2025 report in Scientific Reports highlights NEOM’s achievements:
"The success of NEOM's AI-driven approach illustrates the transformative potential of ML in shaping sustainable, intelligent urban environments."
In Shanghai, Metropolitan Central Plaza has implemented an AI-driven system that uses sensor data - covering visuals, acoustics, and environmental factors - to dynamically adjust space configurations in real-time. This approach has reduced operational costs by 22.3% and improved space utilization efficiency by 34.2%. These examples show how AI can optimize both environmental outcomes and resource management.
On a broader scale, AI is helping cities around the world address emissions challenges. For instance, graph deep learning models applied to Melbourne, New York, Seattle, Singapore, and Washington DC explained 78.4% of the variation in building operating carbon emissions. This kind of analysis gives urban planners the insights they need to tackle the root causes of emissions effectively.
Community Engagement in Urban Design
Getting a broad and diverse group of residents involved in urban design is no easy task. Traditional public meetings often draw only a small, unrepresentative portion of the community. The voices heard in these settings may not reflect the full spectrum of neighborhood perspectives. But AI is starting to change the game by simulating how thousands of residents from different backgrounds might react to proposed developments.
Simulating Community Responses
AI systems are now capable of modeling entire communities by creating virtual residents with diverse characteristics. These virtual agents can engage in debates about proposals, surfacing concerns that might otherwise go unnoticed by planners.
In February 2024, Zhilun Zhou and his research team from Tsinghua University tested an LLM-based framework across two regions in Beijing. The system simulated thousands of residents from varied backgrounds and used a "fishbowl discussion mechanism." In this setup, a subset of agents actively discussed land-use plans while others observed, generating actionable feedback. Impressively, the framework surpassed human experts in metrics like service accessibility and ecological considerations.
At Kendall Square in Cambridge, Massachusetts, AI agents representing different stakeholder groups voted on development proposals. Adding demographic data into the mix produced more distinct and consistent opinions.
"Multi-agent communication improves the qualities of the arguments of the generated agents... communication and idea exchange help agents to provide richer, more innovative, and inclusive reasoning." - Jin Gao, Researcher
In another example, researchers simulated 30 virtual residents in Beijing's Huilongguan community in December 2024. One agent’s suggestion to increase open space led to a redesign of zone a12, boosting the living experience score to 69.03%.
These simulated interactions are giving planners valuable insights, allowing them to refine proposals before moving on to visual implementation.
Visualizing Development Proposals
After gathering feedback through simulations, AI tools are helping make development proposals more accessible to the public. Zoning rules and architectural plans can be hard for non-experts to grasp, but AI-generated 3D visualizations are making these concepts easier to understand.
In July 2024, Esri’s AI Prototypes team unveiled the Urban Massing Generator (UMG), a tool that uses generative AI to create 3D building models from simple street layouts and zoning data. During a demonstration in Paris, planners could add streets or change zoning categories - like switching to "Mixed-residential" - and the AI instantly generated taller, commercially styled buildings that aligned with patterns from well-planned cities.
Later that year, the City of Montréal introduced a conversational AI agent built with Microsoft Copilot Studio to help residents navigate municipal content. By integrating custom entities such as "Postal Code" and "Borough", the system provided location-specific information, like waste collection schedules and permit details. Solution Architect Mohamed Arhab noted the tool achieved a 90% efficiency rate and citizen satisfaction scores exceeding 4 out of 5 stars.
"One key reason we chose Copilot Studio was the option to easily combine classic, prebuilt responses of a chatbot with the AI-generated responses of an agent. This hybrid option enabled us to achieve a higher level of accuracy than just using generative AI alone." - Mohamed Arhab, Solution Architect, IT Department of the City of Montréal
These advancements in visualization and engagement are breaking down technical barriers, making it easier for communities to participate in urban planning. By enabling faster planning cycles with transparency and continuous feedback, these tools are shaping more inclusive and effective outcomes.
Conclusion
The examples throughout this article highlight how AI agents are revolutionizing urban planning. In Shanghai's Metropolitan Central Plaza, AI-driven responsive design led to a 34.2% boost in space utilization efficiency and a 28.7% improvement in pedestrian flow. Over in Cascais, Portugal, an AI-optimized waste management system is saving the city €600,000 annually while slashing CO₂ emissions by 350 tons. These advancements showcase how AI can tackle a wide range of urban challenges with impressive results.
Beyond operational improvements, cities like Montréal and Helsinki are enhancing citizen engagement with AI-powered tools. In Montréal, a conversational agent now handles 85% of municipal inquiries with an accuracy rate of 95%. Meanwhile, Helsinki has deployed a network of virtual assistants that manage 300 customer interactions daily. These systems not only ensure residents have 24/7 access to essential services but also allow human staff to focus on more complex, high-priority tasks.
The shift from static urban planning to dynamic, continuously optimized digital twins further underscores the transformative role of AI. Cities such as Seoul and Beijing are leading the way, demonstrating how real-time, data-driven optimization can elevate urban performance.
With 66% of cities already investing in AI and 80% planning to do so by 2024, the evidence is clear: AI technologies are delivering measurable improvements in efficiency, planning, and overall city management. These results illustrate the tangible impact AI is having on urban planning today.
Learn more about how NAITIVE AI Consulting Agency can help transform urban planning with autonomous AI agents by visiting naitive.cloud.
FAQs
How is AI transforming traffic management in cities?
AI is transforming urban traffic management by replacing outdated, static systems with smarter, real-time solutions. These advanced systems leverage data and adapt to changing conditions to optimize traffic flow, ease congestion, and lower emissions. For example, combining reinforcement learning with digital-twin simulations allows for precise signal timing adjustments, while adaptive signal control systems - like those used in Tucson - have cut vehicle delays by around 24%, boosting overall traffic efficiency.
Modern AI-driven traffic management centers take this further by integrating data from cameras, sensors, and connected vehicles. This enables them to predict traffic patterns, quickly detect incidents, and send automated alerts to drivers. Beyond improving mobility and safety, these systems also deliver cost savings by cutting fuel use and reducing crash-related expenses. NAITIVE AI Consulting Agency works with municipalities to design and implement these advanced solutions, helping cities unlock their full potential.
How is AI used to predict housing and energy needs in cities?
AI is transforming how we forecast housing and energy needs by breaking down complex data patterns into clear, actionable insights for urban planning. When it comes to housing, AI models dig into factors like population growth, zoning laws, and market behavior to predict where new homes are needed, how many, and what types would be most suitable. This enables city planners to spot potential shortages early and make informed decisions about land use and development strategies.
For energy planning, AI taps into data like weather predictions, building usage, and past energy consumption to model how much energy a city will need and when. These insights highlight ways to improve energy efficiency - whether through retrofits, shifting energy loads, or optimizing heating, cooling, and lighting systems. By doing so, AI not only addresses immediate energy demands but also supports long-term goals for resource conservation.
NAITIVE AI Consulting Agency specializes in delivering integrated AI solutions that combine these forecasting tools, helping U.S. cities turn data insights into smart strategies for managing both housing and energy challenges effectively.
How does AI improve community engagement in urban planning?
AI is reshaping how communities engage with urban planning by fostering continuous, inclusive communication with residents. Take multilingual virtual assistants, for example. These digital helpers are available 24/7 to answer questions, translate requests, and guide users to relevant services. This makes it easier for non-English speakers and those who can't attend in-person meetings to participate. Plus, these assistants collect real-time feedback, allowing planners to spot concerns and trends much faster than with traditional methods.
AI tools also streamline decision-making by giving stakeholders a way to weigh in on land-use scenarios. This helps balance competing interests and encourages fair outcomes. With real-time data analysis, public spaces can evolve to meet changing community needs. For instance, cities like San Jose and Bowling Green have successfully implemented AI-driven tools, resulting in greater resident engagement and satisfaction.
NAITIVE AI Consulting Agency takes this a step further by offering customized AI solutions for municipalities. Their services include virtual assistants and decision-support systems designed to integrate local data and feedback. By doing so, NAITIVE helps cities create transparent, inclusive planning processes where every voice counts.




