AI Agents: The Updates
This week’s platform updates show AI agents moving into production—boosting automation, cutting costs, and improving workflows amid data and integration hurdles.

AI agents are no longer just experimental tools - they are now integral to industries like supply chain, customer service, and healthcare. This week, major updates from platforms like LangChain, OpenAI, and Langflow highlight how businesses are using AI to automate workflows, cut costs, and improve efficiency. Key developments include:
- LangChain & LangGraph: Reached version 1.0, offering API stability with 90M monthly downloads and adoption by companies like JP Morgan and Cisco.
- Google's Gemini 3 Pro: Boosts reasoning success rates by 17% with new control parameters.
- OpenAI's AgentKit: Introduced a visual Agent Builder and "computer use" tools, achieving 87% success on web benchmarks.
- Langflow 1.7: Added tools like CUGA for complex tasks and ALTK for tool validation, along with local GPU integrations to reduce costs and enhance privacy.
- n8n Updates: Improved workflow execution speed, added AI workflow evaluation, and addressed a critical security vulnerability.
Businesses are leveraging these tools to streamline processes - like Oracle automating supply chain tasks and Zendesk resolving 80% of customer service interactions autonomously. While adoption is growing, challenges like data quality and system integration remain key hurdles.
Takeaway: Companies investing in AI agents now are gaining a competitive edge, with early adopters already seeing measurable benefits like reduced costs and faster workflows.
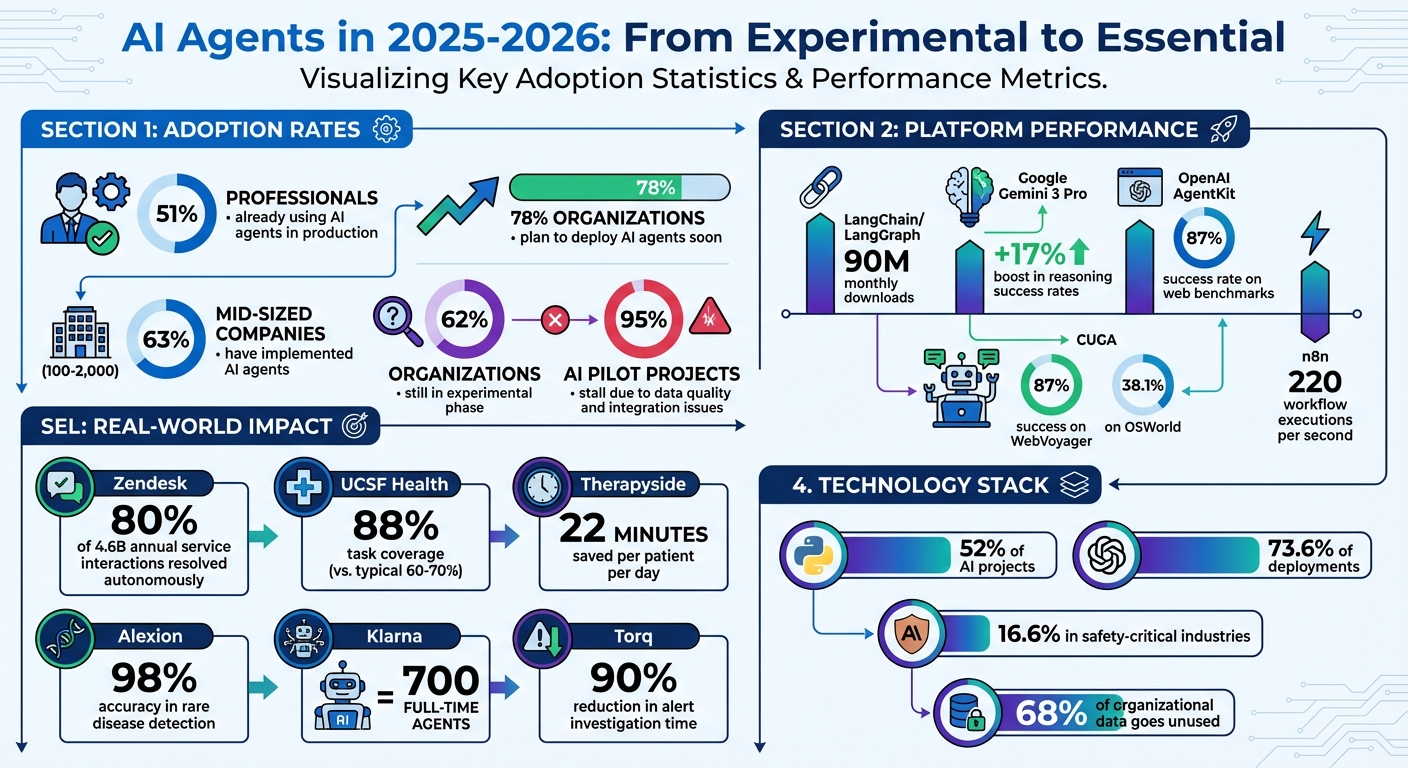
AI Agent Adoption Statistics and Platform Performance Metrics 2025-2026
The Agent Factory: Building a Platform for Enterprise-Wide AI Automation
Latest Updates in AI Agent Platforms and Tools
This section dives into recent advancements in AI platforms, showcasing updates that are reshaping automation across industries.
Langflow: Advancing Workflow Automation
Langflow 1.7 has rolled out new enterprise-level agent components aimed at tackling complex automation challenges. Among its key features is CUGA (Configurable Generalist Agent), an IBM Research framework designed to handle intricate tasks such as navigating web browsers and generating custom API interaction code. Impressively, CUGA achieved an 87% success rate on WebVoyager and 38.1% on OSWorld.
Another highlight is the ALTK (Agent Lifecycle Toolkit), which addresses the issue of invalid tool calls in production environments. ALTK leverages SPARC for tool validation and refines API data through intelligent JSON post-processing, ensuring context windows remain uncluttered. Phil Nash, Developer Advocate, shared:
Langflow 1.7 brings Streamable HTTP support for MCP clients and servers, two new research-backed agent components (ALTK and CUGA), and webhook authentication.
For businesses aiming to balance performance and cost, the new LLM Selector is a game-changer. This feature dynamically routes tasks to the most suitable model based on factors like quality, speed, or cost. Additionally, Langflow now connects to over 500 AI models via the CometAPI and integrates Amazon Bedrock through the Amazon Bedrock Converse API. Enhanced production readiness includes webhook authentication with API key requirements and AWS S3 storage for file uploads, moving beyond local-only setups.
These updates emphasize Langflow's commitment to streamlining workflows and optimizing costs, setting a new standard for AI-driven automation.
n8n: Low-Code Automation Enhancements
n8n continues to bridge visual workflow design with powerful automation tools. The platform now supports up to 220 workflow executions per second on a single instance using queue mode, making it ideal for high-demand operations. Recent updates introduced AI workflow evaluations (June 2025) to simplify interpreting complex agent outputs, along with dedicated AI nodes and LangChain integration for building multi-step agents.
To address privacy concerns, the Self-Hosted AI Starter Kit enables enterprises to run LLMs locally, ensuring full control over data flow and compliance with data residency requirements. Governance features have also been upgraded, including Git-based source control, credential sharing, and SOC 2 compliance. However, in January 2026, n8n identified a critical CVSS 10.0 Remote Code Execution vulnerability, urging immediate updates for both self-hosted and cloud versions.
With these improvements, n8n strengthens its position as a reliable low-code automation platform for businesses of all sizes.
OpenAI Agents SDK: Expanding Development Possibilities
OpenAI's AgentKit suite has introduced a visual Agent Builder and "computer use" capabilities, achieving an 87% success rate on web interaction benchmarks. The SDK is compatible with models from other providers that support a Chat Completions-style API, offering developers flexibility in choosing models.
The availability of Reinforcement Fine-Tuning (RFT) has expanded, now generally accessible for OpenAI o4-mini and in private beta for GPT-5. Meanwhile, the computer use tool, currently in a research preview, is available to select developers in usage tiers 3-5 through the Responses API. The visual canvas approach of the AgentKit suite aligns product, legal, and engineering teams during development, resulting in measurable efficiency improvements for enterprise applications.
These updates from OpenAI highlight the growing capabilities of their SDK, offering developers more tools to create effective and adaptable AI solutions.
Current Trends in AI Agent Adoption
AI agents are evolving from experimental prototypes to reliable, production-ready tools. This transformation is largely fueled by the untapped potential of organizational data - about 68% of it goes unused. Multimodal agents, capable of analyzing emails, Slack messages, and PDF documents, are stepping in to fill this gap.
Enterprise AI Consulting and Automation
The way enterprises approach AI agents has shifted dramatically. Instead of focusing on isolated tasks, companies are now tackling strategic projects that deliver measurable returns on investment (ROI). Python plays a key role in 52% of these projects, with OpenAI powering 73.6% of deployments. Meanwhile, Claude is favored in 16.6% of safety-critical industries.
A growing trend in enterprise systems is the orchestration of multiple specialized agents. These "teams" of agents - such as research, writing, and review agents - work together like microservices to manage intricate workflows. However, this requires robust governance frameworks. Harrison Chase, CEO of LangChain, highlighted the importance of advanced models in this space:
The new Gemini model is a strong step forward for complex, agentic workflows - especially for those who need sophisticated reasoning and tool use.
Standardization is also gaining momentum. The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is emerging as a shared framework for connecting agents to tools and data, with backing from major players like OpenAI, Microsoft, and the Linux Foundation. Organizations are implementing "control planes" - such as Microsoft Agent 365 or AWS Bedrock AgentCore - to manage permissions, audit trails, and safeguards against "reasoning drift". This focus on governance and standardization is paving the way for tailored, industry-specific solutions.
Industry-Specific AI Agents
Specialized agents are making a tangible impact across various sectors, building on enterprise-level strategies. For instance, in early 2024, Klarna deployed an OpenAI-powered support agent that resolved two-thirds of customer service tickets, effectively handling the workload of 700 full-time agents.
In healthcare, Therapyside introduced "Maia" in June 2025, a reasoning agent developed with NVIDIA's NeMo Agent toolkit. This agent streamlines administrative tasks like scheduling and payment tracking, saving clinicians 22 minutes per patient per day. Similarly, the pharmaceutical sector is benefiting from AI innovations. Alexion, AstraZeneca's rare disease division, collaborated with Pangaea Data to implement an AI system that achieved 98% accuracy in identifying critical data points for rare disease detection. It also reduced the configuration time for clinical calculators from weeks to just days.
These specialized agents are often built using pre-configured components, giving developers the tools to create solutions tailored to industries like automotive, manufacturing, and life sciences.
Meanwhile, voice interfaces are becoming indispensable in high-stakes fields like healthcare and finance. These sectors are moving beyond traditional text-based chatbots to adopt low-latency voice agents that handle real-time, complex interactions. This shift reflects a broader trend: replacing single, overburdened agents with "crews" of domain-specific experts, which simplifies operations and enhances reliability.
How Businesses Are Using AI Agents
With recent advancements in AI platforms, businesses are seeing real-world benefits by integrating AI agents into their operations. A survey reveals that 51% of professionals are already using AI agents in production, while 78% of organizations plan to deploy them soon. Among mid-sized companies (those with 100–2,000 employees), 63% have already implemented AI agents. These numbers highlight how AI is becoming a key player in areas like supply chain management and customer service.
Case Study: AI Agents in Supply Chain Management
AI is reshaping supply chain operations, bringing efficiency and automation to traditionally time-consuming tasks. Oracle, for instance, has integrated AI agents into its Fusion Cloud Applications to streamline administrative work. Chris Leone, Executive Vice President of Applications Development at Oracle, shared:
Supply chain professionals often spend several hours every week on administrative tasks, such as data analysis, policy reviews, and order processing.
These AI agents handle procurement by extracting supplier quotes from emails, creating purchase requisitions, and comparing factors like technical specs, costs, and lead times to help sourcing decisions. For inventory management, they monitor stock levels in real time, suggest approved substitutes during shortages, and analyze expiring inventory to trigger actions that minimize waste.
Manufacturing processes also benefit from tools like "Disposition Assistants", which evaluate rejected items and recommend fixes based on historical data. In logistics, AI agents ensure outbound shipments meet regulatory standards for hazardous materials and speed up the pick, pack, and ship cycle for urgent orders. Some companies are even using platforms like n8n to build AI-powered control towers, connecting warehouse and transport systems. These agents can process natural language requests, generate SQL queries, and provide actionable insights directly to managers.
Customer Service with AI Voice Agents
AI voice agents are revolutionizing customer service by going beyond basic chatbots to handle complex, multi-step tasks. In March 2025, Zendesk partnered with OpenAI to pilot AI agents powered by GPT-4o. These agents could independently plan and execute responses, significantly reducing setup time from days to minutes. The results were impressive: 80% of service interactions - out of a staggering 4.6 billion annually - were resolved autonomously. As Zendesk CTO Adrian McDermott explained:
The old world was message in, response out. Real customers change their minds, ask clarifying questions, and expect the AI to follow along naturally. In service, the only outcome that matters is resolution.
Healthcare providers are also leveraging these tools. In late 2025, UCSF Health tested Salesforce's Agentforce Voice for patient service calls. By running thousands of synthetic conversations simulating various accents and background noise, the AI achieved 88% task coverage, far exceeding the typical 60% to 70% of traditional systems. These agents now handle tasks like appointment scheduling, insurance verification, and basic medical inquiries 24/7, allowing clinical staff to focus on direct patient care.
Practical Advice for Implementing AI Agents
Successfully implementing AI agents requires a thoughtful approach that aligns your infrastructure, governance, and specific requirements. These tips build on the advancements mentioned earlier and offer practical steps for enterprise applications. As Carlyle shared:
The evaluation platform cut development time on our multi-agent due diligence framework by over 50%, and increased agent accuracy 30%.
This guidance helps establish a solid foundation for streamlined and effective AI operations.
Building a Unified AI Platform
Start by identifying key requirements like data residency, compliance needs, and whether deployment will be cloud-based or on-premise. Once these factors are clear, you can select the right tools. Options like n8n or Langflow are great for rapid prototyping with visual interfaces, while code-first tools like LangGraph or CrewAI offer precise control for handling complex workflows.
A unified platform should also break down complex agents into smaller, specialized units, allowing for smoother collaboration and integration as workflows progress. To ensure consistency, set up a centralized registry to manage data and tool integrations across your organization.
Managing Governance and Compliance
Governance should be integrated from the start. Modern frameworks now include safety checks that validate both inputs and outputs, helping prevent policy violations. For enterprise use, features like Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), Single Sign-On (SSO), and detailed audit logs are essential. Observability is equally critical - tools like LangSmith or Langfuse can track agent performance, troubleshoot issues, and monitor token costs in real time.
For tasks involving sensitive data, consider adding Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) checkpoints, where human approval is required before an agent’s recommendation is acted upon. If data privacy is a priority, self-hosted solutions are worth exploring. For example, deploying local models like Ollama with Langflow supports zero-trust architectures by keeping sensitive information on-device.
While governance is key, managing costs is just as important for long-term AI success.
Cost-Effective Implementation Approaches
To get the most value out of your AI investment, adopt a multi-model strategy. Use advanced models like GPT-4o or GPT-5 for complex reasoning tasks, while relying on faster, more affordable models like GPT-5-mini for simpler interactions. Visual builders can also save time and money, especially for teams with limited technical expertise. As Ramp noted:
Agent Builder transformed what once took months of complex orchestration, custom code, and manual optimizations into just a couple of hours.
Choosing model-agnostic frameworks like Langflow or CrewAI allows flexibility to switch providers as pricing or capabilities evolve. Start with flagship models to establish a performance baseline, then optimize for cost efficiency once you know what works. Additionally, structured outputs - such as strict JSON schemas - can simplify integration with other systems and reduce errors.
Finally, set up evaluation pipelines early on. Use datasets and automated graders to measure agent accuracy and refine prompts with human feedback. This approach ensures your AI agents not only perform well but also remain cost-efficient over time.
Conclusion
This week's updates highlight a crucial transition: AI tools are no longer just experimental - they’re becoming indispensable across industries like retail, security, and operations. A prime example is Google’s Universal Commerce Protocol, launched on January 11, 2026. With major retailers on board, autonomous agent-to-agent commerce has officially entered the mainstream. Similarly, McKinsey’s rapid leap from 3,000 to 20,000 AI agents in just 18 months shows how quickly enterprises can scale when foundational challenges are addressed.
That said, hurdles still exist. While adoption rates are climbing, nearly 95% of AI pilot projects stall due to issues like poor data quality and system integration. These barriers emphasize the importance of solid data infrastructure and human oversight from the very beginning.
The importance of strategic planning is evident in success stories like Torq, which achieved a 90% reduction in alert investigation time and reached a $1.2 billion valuation in January 2026. Similarly, XPENG’s upcoming launch of VLA 2.0 with Level 4 autonomous driving in March 2026 underscores how early adopters can pull ahead of competitors.
For businesses, the takeaway is clear: those that prioritize data quality and prepare their systems for seamless AI agent collaboration , such as building multi-agent research teams, will gain a significant edge. With 62% of organizations still in the experimental phase, the opportunity for first-mover advantage is ripe.
FAQs
How are businesses addressing challenges with integrating AI agents?
Businesses are addressing the challenges of integrating AI agents by shifting to modular, team-based architectures. Instead of relying on a single, overburdened agent, they assign specific tasks - like contract review, customer support, or data extraction - to specialized agents. This strategy not only reduces processing delays but also cuts costs and boosts efficiency. These agents collaborate effectively through orchestration platforms, which handle communication, task transitions, and shared workflows in a visual, low-code interface.
Integration has also been streamlined by standardized tools and protocols, such as OpenAI’s APIs and Microsoft’s frameworks. These tools enable secure connections with existing systems like SaaS platforms and ERP software. Features like policy enforcement, audit tracking, and model management ensure compliance while speeding up deployment.
To strike the right balance between speed and scalability, businesses are leveraging frameworks that cater to both. Low-code tools enable rapid prototyping, while enterprise-grade platforms support large-scale deployments with strong governance. The results? Faster outcomes, greater accuracy, and major cost savings - some companies have reported cutting operational expenses by as much as 75% after implementing coordinated AI agent teams.
What are the benefits of using specialized AI agents in different industries?
Specialized AI agents are designed to excel at specific tasks, whether it's managing customer inquiries, analyzing data, or organizing schedules. Unlike broader, general-purpose AI models, these targeted agents are built for efficiency. They help cut costs and enhance reliability by focusing solely on well-defined workloads.
To make these agents work together seamlessly, organizations use orchestration frameworks. These frameworks allow the agents to collaborate effectively and share relevant context. This approach has proven especially useful in industries like finance, healthcare, and supply chain management, where tailored AI solutions are key to meeting unique operational demands - all while maintaining scalability and performance.
With more businesses integrating these specialized agents into their operations, they’re becoming a cornerstone of automation strategies. The benefits? Quicker decision-making, actionable insights, and smooth compatibility with existing tools.
How can businesses maintain data quality and integrate systems effectively for AI agents?
To build reliable AI agents, businesses need to emphasize data quality and smooth system integration. Begin by establishing clear data contracts. These should include schemas, validation rules, and metadata to minimize errors. By embedding these checks into workflows, you can catch potential issues early, ensuring that your AI systems receive accurate and clean inputs.
When it comes to integration, having a centralized connector catalog can make a big difference. This catalog streamlines how tools like CRM, ERP, and knowledge bases connect, allowing developers to reuse secure, pre-approved integrations. Using low-code platforms with pre-built components can also speed up prototyping while simplifying error management.
Lastly, focus on monitoring and governance. Implement tools for logging, version control, and rollback capabilities in your production pipelines. These measures ensure your AI agents work with dependable data and integrate seamlessly with existing systems, providing consistent and reliable outcomes for businesses of any size.




